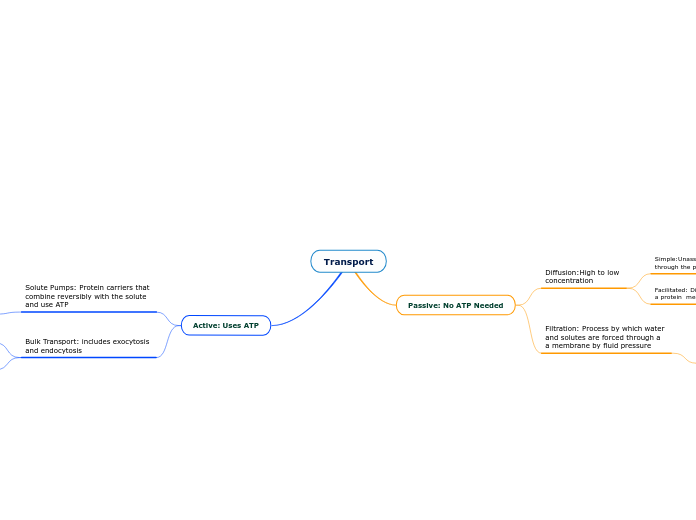
Transport
Active: Uses ATP
Bulk Transport: includes exocytosis
and endocytosis
Endocytosis moves substances into the cell by
packaging them into vesicles
Pintocytosis: The cell membrane takes in a droplet of
extracellular fluid containing dissolved proteins or fats
Exocytosis moves substances out of cells packaging
them into vesicles
Phagocytosis: Cytoplasmic extensions engulf large
particles such as bacteria or dead body cells
Solute Pumps: Protein carriers that
combine reversibly with the solute
and use ATP
Examples of this are sodium-potassium pumps.
They simultaneously carry sodium ions out and
potassium ions into the cell. This is necessary
for the transmission of the nerve impulses
Passive: No ATP Needed
Filtration: Process by which water
and solutes are forced through a
a membrane by fluid pressure
Hydrostatic pressure is usually exerted
by blood. A pressure hradient pushes
solute-containing fluid from the higher-pressure
area to the lower-pressure area.
Ex: Kidneys
Diffusion:High to low
concentration
Facilitated: Diffusion of substances using
a protein membrane channel
Used because the solid is too large or lipid
insoluble
Simple:Unassisted diffusion of solutes
through the plasma membrane
Osmosis: The diffusion of water through
the membrane. Aquaporin makes it easier
for water to get through