https://www.zurich.com/es/knowledge/articles/2015/01/the-risks-of-rapid-urbanization-in-developing-countries
http://geographyfieldwork.com/urban_geography_glossary.htm
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fKnAJCSGSdk&list=PLAoO2mx2v58dGeAnzgHb0rFOan9GtDyMh
Urbanization
urbanization noun
also British urbanisation /ˌɚbənəˈzeɪʃən/
Learner's definition of URBANIZATION
[noncount]
- : the process by which towns and cities are formed and become larger as more and more people begin living and working in central areasrapid urbanization
- the effects/process of urbanization
— urbanize also British urbanise /ˈɚbəˌnaɪz/ verb urbanizes;urbanized; urbanizing
- [no object]The country/region is rapidly urbanizing.
- [+ object]farmland that is being urbanized
— urbanized also British urbanised adjective [more urbanized; most urbanized]
- an urbanized area/society
CHANGING FORMS
CLASSIFICATION
HISTORIC GROWTH OF AREAS
IMMIGRATION
STYLE OF ARCHITECTURE and PLANNING METHODS
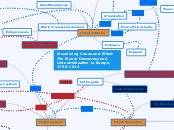
CONSECUENCES
HEALTH AND SOCIAL EFFECTS
POSITIVE EFFECTS
CHANGES
Dietary and Exercise Patterns
IMPROVEMENTS
Access to health care
Sanitation
Public hygiene
INCREASED LIFE EXPECTACY
NEGATIVE EFFECTS
Contagious diseases
Non-communicable diseases
Increased mortality
ENVIRONMENTAL EFFECTS
REDUCTION OF DESTRUCTIVE FARMING TECHNIQUES
DAMAGES IN THE ECOSYSTEM
ECONOMIC EFFECTS
OPPORTUNITIES
TRANSPORTATION
HOUSING
EDUCATION
JOBS
REDUCTION OF EXPENSES
COMMUTING AND TRANSPORTATION
SUBURBANIZATION
MARGINALIZATION
Slums
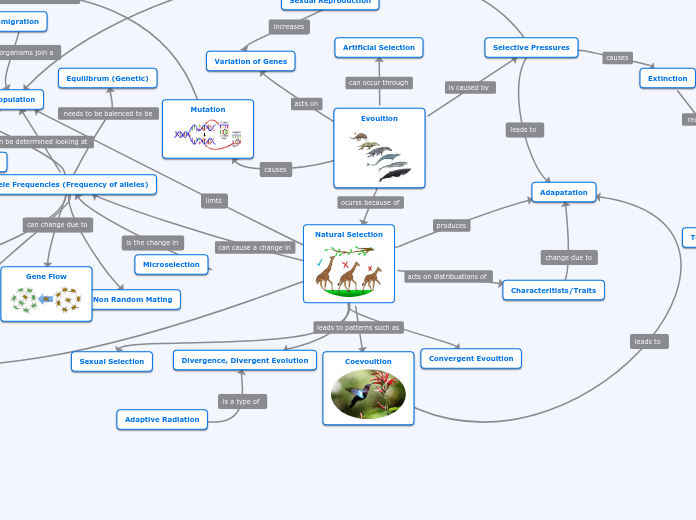
CAUSES
GLOBALIZATION
RURAL FLIGHT
COMMERCIAL FLIGHT
INDIVIDUAL ACTIONS
GOVERNMENT and SOCIAL ACTIONS
PROCESS OF POPULATION CONCENTRATION IN SOCIETY
INHERENT TENDENCY IN SOCIETY
PROCEED UNTIL IT IS INHIBITED BY ADVERSED CONDITIONS
INCREASE IN SIZE OF INDIVIDUAL CONCENTRATIONS
MULTIPLICATION OF POINTS OF CONCENTRATION
COUNTRIES
DEVELOPING COUNTRIES IN ASIA
DEVELOPING COUNTRIES IN AFRICA
POPULATION GROWTH
DRAWBACKS
EXCLUSION and MARGINALIZATION
EXTREME POVERTY
SLUM GROWTH
Slum growth -which is not the same as
urbanization- results from the decisions to limit poor people’s access to cities, through limited service provision to informal settlements or by forced evictions and resettlement of the urban poor to peripheral or under-serviced areas. - See more at: http://www.unfpa.org/urbanization#sthash.yvmSXGaH.dpuf
INEQUALITY AND VULNERABILITY
Phenomenon: URBAN SPRAWL
Urban land is expanding much faster than urban population - See more at: http://www.unfpa.org/urbaniz
ation#sthash.yvmSXGaH.dpuf
It can eliminate opportunities
Risky and unhealthy living conditions
High vulnerability to disasters
Heavy pollution
Women with ferlitity rates similar to women in rural areas
Access to health facilities
BENEFITS
SUSTAINABILITY
CREATE MORE SUSTAINABLE LAND
USE RESOURCES MORE EFFECTIVELY
SOCIAL TRANSFORMATION
CITY
OPPORTUNITIES FOR WOMEN´S EMPOWERMENT
ACCESS TO EDUCATION AND HEALTH SERVICES
REALIZATION OF WOMEN´S REPRODUCTIVE RIGHTS
PROMOTING WOMEN´S EMPOWERMENT
SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH CARE
SOCIAL MOBILIZATION (PROXIMITY)
ENVIRONMENTAL TRANSFORMATION
PROTECT BIODIVERSITY OF NATURAL ECOSYSTEMS
ECONOMIC TRANSFORMATION
OPPORTUNITIES IN THE CITIES
ECONOMIC GROWTH
JOBS - MARKETPLACE COMPETITION