A HISTORY OF MIGRATION
In physics, energy is the quantitative property that must be transferred to an object in order to perform work on, or to heat, the object. Energy is a conserved quantity; the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed
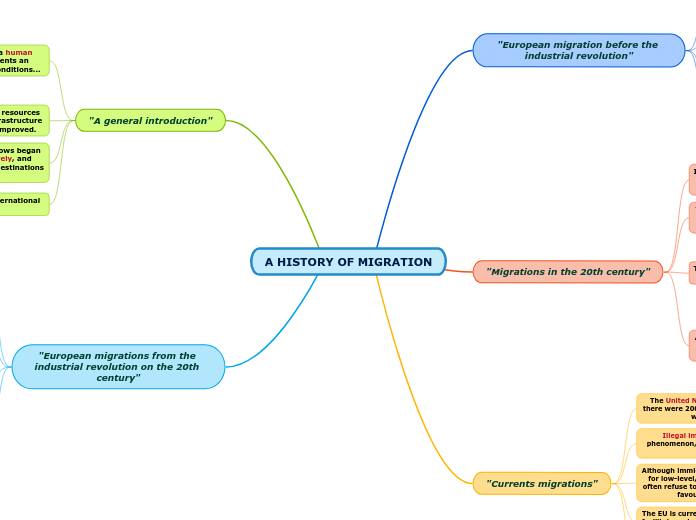
"European migrations from the industrial revolution on the 20th century"
Among other destinations, a flood of emigrants left for:
Australia and New Zealand.
-Brazil;
-Canada;
-Argentina and Uruguay;
-The USA;
Emigration to the US was three times greater than emigration to any other destination.
Thanks to the development of infrastructure such as steamships, Europe's labour surplus could be transferred between continents more easily than ever before...
In the 19th century Europe became increasingly urbanised and growing manufacturing and service industries replaced agricultural activity.
This encouraged migration!
In the second half of the 19th century, promising new territories attracted large numbers of poor European immigrants.
Offered the opportunity to cultivate land and extract raw material.
-South Africa...
-Australia;
"A general introduction"
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time. A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery.
As a consequence of the new international migrations..
There is a serious political conflict between the migrants' destination countries and their places of origin.
In most countries, these governmental migration policies have recently become more rigorous and selective.
In the 19th century, migratory flows began to flow more rapidly and intensively, and had a new impact on both their destinations and their places of origin.
Thermal energy storage is achieved with widely differing technologies.
Depending on the specific technology, it allows excess thermal energy to be stored and used hours, days, months later, at scales ranging from the individual process, to building or town.
What are 3 types of thermal energy?
More recent migration flows were often directed:
Were linked to manufacturing and trade activities.
Towards urban areas;
In the modern age (1492-1789) resources increased and both transport infrastructure and means of communication improved.
The battery acquires its charged condition either by recharging or in the manufacturing of the unit.
During discharge, the chemical on the anode releases electrons, and ions in the electrolyte undergo an oxidation reaction.
Name the particular compounds in which energy is stored:
Eurasia, Africa and America were all linked by maritime transport.
Moving between territories is a human prerogative because it represents an opportunity to improve living conditions...
Flywheel energy storage (FES) works by accelerating a rotor to a very high speed and maintaining the energy in the system as rotational energy.
Write down the main components of a typical flywheel.
Caused empty territories to settle;
Encouraged the spread of agriculture;
Allowed it to disperse across continents;
It has enabled mankind to survive;
"Currents migrations"
The history of the 20th century has shown that temporary migration actually tends to become permanent.
From 1945 to 1973, streams of Turks moved to Germany for temporary manual work and eventually settled and formed a large community that still constitutes a quarter of the total foreign labour force in Germany.
The EU is currently considering a 'blue card' to facilitate and guarantee the income of its most qualified and specialised migrants.
Although immigrants help to meet the demand for low-level, low-paid jobs that Europeans often refuse to do, European countries tend to favour 'circular migration'...
These are temporary and often seasonal flows of unskilled workers.
Illegal immigration is a widespread phenomenon, affecting most of the Western world.
In 2011, the Arab Spring caused a wave of emigration, especially in the Mediterranean area. Most of the refugees and migrants in these flows tried to enter Europe illegally.
The United Nations estimates that in 2010 there were 200 million migrants, or 3% of the world's population...
In the same year, there were 25 million non-Europeans in Europe, or 5% of the European population.
"Migrations in the 20th century"
After the oil crisis of 1973-74, a new phase of economic reconstruction put an end to mass internal migration in Europe.
The process of globalisation has progressively increased the number of countries of emigration, which now include nations in:
-South-East Asia.
-the Middle East;
-South America;
-Africa;
The world wars caused internal migration in Europe...
People left poorer places to settle in richer, more industrialised ones.
Have been considered 'double migration' countries, because they experienced internal migration from the south to the north and migration to other countries.
-Spain;
-Italy;
The First World War and migration policies drastically reduced the scope of transcontinental migration.
In the United States, for example, the National Origin Act of 1924 set a 'cap' on the maximum number of migrants allowed into the country.
In the 20th century, the foreign demand for European labour decreased and the rate of population growth in Europe slowed down.
"European migration before the industrial revolution"
There are many different types of energy, which all fall into two primary forms – kinetic and potential.
Energy can transform from one type to another, but it can never be destroyed or created.
Transoceanic migration began after 1500 and Europe became the source of new waves of migration.
Gravitational energy is a form of potential energy.
It is energy associated with gravity or gravitational force, in other words, the energy held by an object when it is in a high position compared to a lower position.
Give examples.
It is estimated that about one million Europeans moved to America in each century between 1500 and 1800.
After the late Middle Ages, the mobility of Europeans increased over short and long distances, thanks to...
Nuclear energy is stored in the nucleus of atoms.
This energy is released when the nuclei are combined (fusion) or split apart (fission).
Nuclear power plants split the nuclei of uranium atoms to produce electricity.
What element do they use to fuel nuclear power plants?
-Improvements in animal-drawn transport.
-Better infrastructure;
-New technological innovations;
In the first millennium A.D., invasions and occupations were the largest migratory flows within Europe...
Thermal energy is created from the vibration of atoms and molecules within substances. The faster they move, the more energy they possess and the hotter they become. Thermal energy is also called heat energy.
Give examples of heat energy.
An example of both is the migration of the Germanic peoples, which occurred after the decline of the Roman Empire in 476 AD.
The typical migration of rural societies has two main characteristics:
Motion energy or mechanical energy is the energy stored in objects; as objects move faster, more energy is stored.
Examples of motion energy include wind, a flowing river, etc.
Give more examples.
Migrants who were able to generate a surplus population that could support further migration.
Experienced migrants, who were able to move to different places and adapt to different environments;