The Advancements of Aboriginal Rights.
1914-1929
WWI
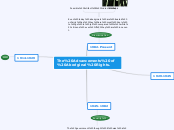
Even during and after the War, they were discriminated. During the war effort they were not allowed to contribute to help the army and they were looked down upon. After the war, there were rewards given to the soldiers to help their own lives after the war, but First Nations did not receive as much as other would.
Possible Artifact: Soldier Settlement Act
Aboriginals were very excited to join the army, but unfortunately, they were not allowed to join, due to them being First Nations. Although a few joined they were saw as the weakest of the army.
1945-1982
Equality?
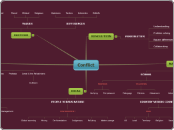
The government thought it was a good idea to bring equality by getting rid of the Indian status. Which brought the White Paper act. In this act, all advantages given to First Nations were to be taken away to make them more equal. The aboriginals saw this as a way for the government to incorporate them into the English Community. The FN then came out with their own paper called the Red Paper.
Possible Artifact: Red Paper
Possible Artifact: White Paper
1929-1945
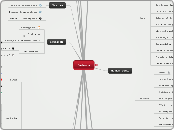
Stripped of their identity
The idea was to get rid of the "Indian" in them. To do this they would get rid of their cultural clothing, cut their hair and remove all personal belongings connecting them to their culture.
Possible Artifact: Residential Schools
If they were to be caught speaking their first language, they would be punished. Many punishments included a beating from the teacher, locked up in a room for days, branded.
1,100 students attended 69 schools across Canada, in 1931, 80 schools were opened and 1,500 First Nations were removed from their homes.
1982-Present
Discrimination
Even today aboriginals are treated unfairly as they are most likely to go to jail compared to white citizens even if they are innocent.
Subtopic
Possible Artifact: Indian Act