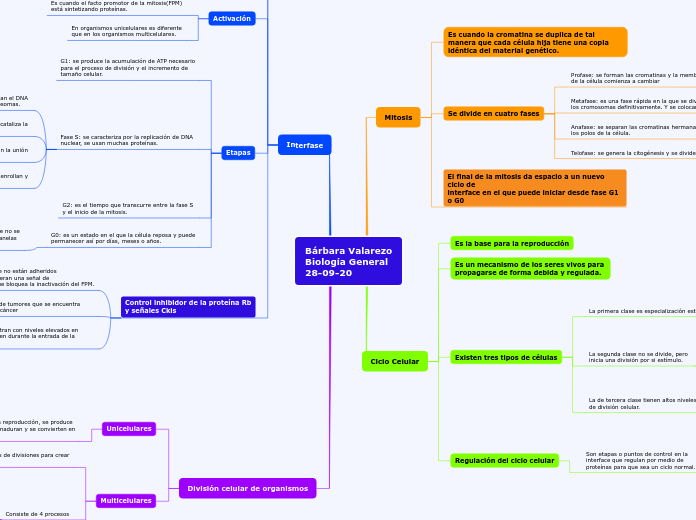
Bárbara Valarezo
Biología General
28-09-20
In linguistics, syntax is the set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a given language, usually including word order.
División celular de organismos
A compound sentence is a sentence that has at least two independent clauses joined by a comma, semicolon or conjunction. An independent clause is a clause that has a subject and verb and forms a complete thought.
Multicelulares
Create your own compound sentences, using the coordinators above.
Consiste de 4 procesos
División celular
Distribución de los cromosomas
Replicación del DNA
Crecimiento celular
Se requiere mpas secuencias de divisiones para crear
un individuo.
Unicelulares
When independent clauses are joined with coordinators (also called coordinating conjunctions), commas and semicolons, they do more than just join the clauses. They add meaning and flow to your writing.
Implica una verdadera reproducción, se produce
dos células hijas que maduran y se convierten en
individuos distintos.
levaduras como la de la cerveza
o del pan
Interfase
A complex sentence is a sentence that contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses.
An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence, but a dependent clause even though it has a subject and a verb cannot stand alone.
Control inhibidor de la proteína Rb
y señales Ckis
Las proteínas Ckis se encuentran con niveles elevados en células en reposo y disminuyen durante la entrada de la mitosis.
La proteína Rb es supresora de tumores que se encuentra alterada en muchos tipos de cáncer
Los cromosomas que no están adheridos
al huso mitótico generan una señal de
retroalimentación que bloquea la inactivación del FPM.
Etapas
An appositive clause follows another noun or noun phrase in apposition to it; that is, it provides information that further identifies or defines it.
G0: es un estado en el que la célula reposa y puede
permanecer así por días, meses o años.
fibras musculares esqueléticas que no se
dividen, pero sí renuevan sus organelas
citoplasmáticas
G2: es el tiempo que transcurre entre la fase S
y el inicio de la mitosis.
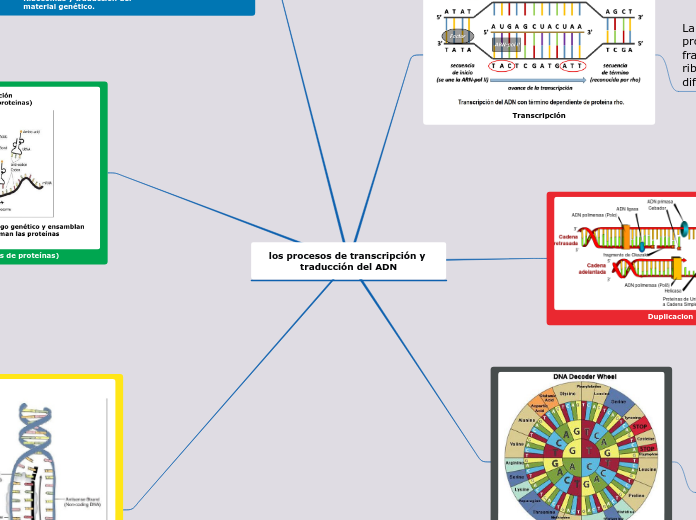
Fase S: se caracteriza por la replicación de DNA
nuclear, se usan muchas proteínas.
Topoisomerasas: enzimas que enrollan y
desenrollan el DNA.
Ligasas: Son enzimas que catalizan la unión
de dos moléculas
Polimerasa: Es una enzima que cataliza la
síntesis de DNA.
Histonas: Empaquetan y ordenan el DNA
en estructuras llamadas nucleosomas.
G1: se produce la acumulación de ATP necesario
para el proceso de división y el incremento de
tamaño celular.
Activación
The subject clause is a dependent clause that acts as a subject.
En organismos unicelulares es diferente
que en los organismos multicelulares.
Es cuando el facto promotor de la mitosis(FPM)
está sintetizando proteínas.
Inactivación
A predicative clause may be introduced by conjunctions - that, whether, whether... or, as, as if, as though, because, lest, the way - or connectives.
The latter may be conjunctive pronouns - who, whoever, what, whatever, which - or conjunctive adverbs - where, wherever, when, whenever, how, why.
Es cuando existe una ausencia de síntesis de proteínas
y la mitosis no se llevará acabo.
Es la fase en la cual la célula crece, se replica
y distribuye.
The object clause is a phrase on which a verb performs an action. It falls at the end of a sentence, and is governed by a verb or a preposition.
Ciclo Celular
Regulación del ciclo celular
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is driving the car with his mother.
Son etapas o puntos de control en la
interface que regulan por medio de
proteínas para que sea un ciclo normal.
Ciclinas: regula la progresión
de la célula durante el ciclo celular.
Cinasas: producen que las células
sean activas o inactivas.
Existen tres tipos de células
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is the driver.
La de tercera clase tienen altos niveles
de división celular.
Células de la sangre
Células epiteliales
La segunda clase no se divide, pero
inicia una división por si estímulo.
linfocitos
hepatcitos
La primera clase es especialización estructural
Gametos
células nerviosas
Es un mecanismo de los seres vivos para
propagarse de forma debida y regulada.
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim drives the car.
Es la base para la reproducción
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim drives.
Mitosis
El final de la mitosis da espacio a un nuevo ciclo de
interface en el que puede iniciar desde fase G1 o G0
Se divide en cuatro fases
The predicate of a sentence is the part that modifies the subject in some way. Because the subject is the person, place, or thing that a sentence is about, the predicate must contain a verb explaining what the subject does and can also include a modifier.
Telofase: se genera la citogénesis y se divide la célula
Anafase: se separan las cromatinas hermanas a
los polos de la célula.
Metafase: es una fase rápida en la que se dividen
los cromosomas definitivamente. Y se colocan en el medio.
Profase: se forman las cromatinas y la membrana
de la célula comienza a cambiar
Es cuando la cromatina se duplica de tal manera que cada célula hija tiene una copia idéntica del material genético.
The subject of a sentence is the person, place, thing, or idea that is doing or being something. You can find the subject of a sentence if you can find the verb.
Ask the question, 'Who or what 'verbs' or 'verbed'?' and the answer to that question is the subject.