door Drew Karaim 5 jaren geleden
231
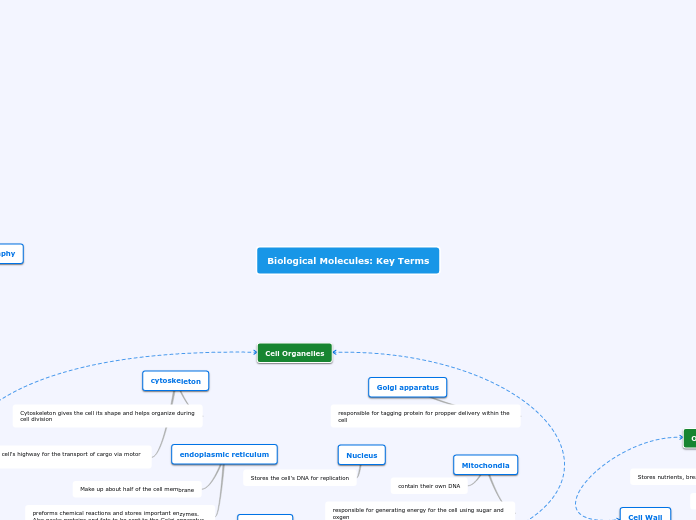
Biological Molecules: Key Terms
Utilizing various imaging and analysis techniques such as X-ray crystallography and electron microscopy allows for the detailed examination of cellular structures and processes. X-ray crystallography uses X-rays with wavelengths comparable to the spacing between atoms in a crystal to generate a pattern that computers interpret into a model of the substance.