Biological Psychology
By:Camryn Wadsworth
& Komal Saleem
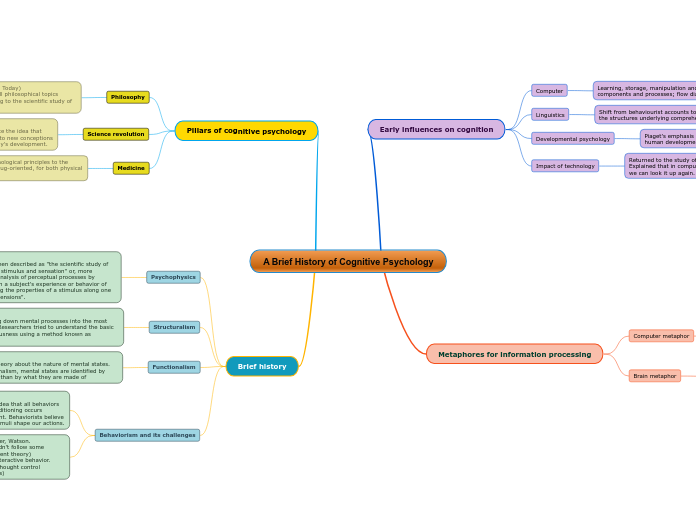
Brain Imaging
Four Neuroimaging techniques
fMRI
Looks at the structure of the
brain and their functions
Uses changes in blood flow to
generate images that show brain
activety and performance
Stands for Functional Magnetic resonance imaging
CAT/CT scans
Stands for Computerized technology
A series of x-rays of the head are
taken from many different directions
Looks at the structure only
Can also be any part of the body, not just the brain
Useful for quick assesing of brain injuries
MRI
Looks at the structure of the
brain, but gets a more details
pictures of the brain tissue
A more detailed 3D image of the
brain and gives a percise mapping
of the physical shape of the brain
Stands for Magnetic resonance imaging
PET
Limitations of a PET Scan
The PET scan does not directly
show the specific area in which
the activity is occurring
Delay in reading the functionsing
of the brain by 40 seconds
PET scans require am ejection of a
radioactive tracer. It allows the
neruoscientist to view the flow of
the blood, oxygen and glucose levels.
This is not recommened for children or adults in great doses
During the PET scan
The part of the brain that shows
less activity is green, blue and puprle
The part of the brain that is showing
the greatest activity shows up as red,
white and yellow
Views the structure of the brain to
see which part if the brain is active
during specific task or events
Stands for Positron Emisson Tomography
Hemispherical Specialization
Both Hemispheres are responsible for different things but
they work together due to the Corpus Callosum
The right hemisphere governs the
left side of the body and the left
hemisphere governs the right side
of the body
Corpus Callosum: is a large bundle of nerve
fibers that connect the left and right
hemisphere and allows them to communicate
Right Hemisphere
Responsible for the creative,
artistic and emotional things
Left Hemisphere
Responsible for the academic,
verbal and analytical things
Structures and functions
Flight or flight response
An evolutionary mechanism that triggers our mind and body to respond to stressful and/or life threatening situations
Limbic System
Amygdala
Two small almond, it is considered the brains alarm system
Plays a major role in the control of emotions. The amyglda forms unconscious memories based on emotional responses
thalamus
Two walnut sized structures joined by a bridge. The thalamus has been said to be the gateway to the cortex. This is the area of the brain that all sensory input goes to before it is sent off to the appropriate region of the brain
hippocampus
Holds the memories from your immediate past and dispatches the memory to the cortex, where it is stores in longterm memory. Once a memory is fully encoded into long term memory, it would appear that the hippocampus is no longer needed for it to be retrieved
Hypothalamus
The pituitary gland controls the functions necessary for maintaining the normal state of the body homeostasis
Plays a role in regulating sex drive, sleep, agressive behaviour and pleasure.
There are 4 lobes:
4.Frontal- Allows us to move parts of our body, think about the past, plan the future, focus attention, reflect, make decision, achieve self-regulation, solve problems, and engage in conversation (Prefrontal Cortex: responsible for impulse control and executive functions. Impulse control)
Prefrontal Cortex is not fully developed until 25 years of age (on average). This part of the brain is newest evolutionarily speaking and responsible for impulse control and executive functions.
3.Parietal- Located at the top of the brain are flat. Responsible for spatial awareness and orientation
2.Temporal- main function is to process auditory stimuli. Responsible for hearing, language, and auditory memories
1.Occipital- located at the lower central back of the brain. Primary function is to process visual information. The visual systems communicates with the other brain regions to determine if it has been stored and if the visual stimuli is meaningful
The Hind Brain
The cerebellum role is coordinates movement and balance
The brain stem consist of the medulla oblongata (lower), the pons (centre) and the midbrain (upper end)
The midbrain processes vision, hearing and eye movement
The medulla oblongata (the lower end)- where the spinal cord meets the brain stem, responsible for basic bodily functions such as heartbeat and respiration,
The pons (center area)- meaning bridge, acts as bridge from the medulla oblongata to the other brain regions, responsible for motor control and sensory analysis, and midbrain (upper end)- processes vision, hearing, and eye movement, the cerebellum- the role is to coordinate movement and balance
Neural Cells
Stem cells
oriiginate in embryos
Researchers can implant stem cells into the nervous system and induce them to grow and replace damaged cells
They can genetically engineered to provide therapy, providing the patient with replacement genes
Have the capacity to differentiate into a more specialzed cell
Our brains have two types of cells. There are the glial cells and the neurons.
Neurons
The neurons are commonly found primarily in the brain and spinal cord (the central nervous system- CNS). Our bodies are capable of generating new neurons, but neurons do not regenerate in the same way as any other cells.
Neurons communicate through chemical and electrical signals. When the neauron becomes stimulated it recieves excitatory signals from another neuron. This results in a neauron being positively charged for a brief period of time known as action potential
Glial Cells
The glial cells are also known as neuroglia. Their function is to guide neurons towards making connections, promote neuronal health, and influence the functioning of the brain. The glial cells do not make their own connections.
Synapses
Neurotransmitters are chemicals in the brain that are generally either excitatory or inhibitory, which means they can either increase or decrease the likelihood of a neuron firing.
Psychoactive drugs interact with neurotransmitters meaning they affect mood, arousal or behaviour. They often allow us to predict how they'll affect us psychologically
opiates such as codeine function as agonists, which means they increase receptor site activiey. Reduce our emotional response to painful stimuli by binding wiht opiod receptoprs and mimicking endorphoins
Neurotransmitters fall into 3 catagories
Peptides
Opioids are an addiction and depression
oxacillin and heroine
Neuropeptides are lumped together loosely under a generic name Endorphins
Endorphins- creates a feeling of euphoria which helps as a pain killer.
Amines
Acetylcholine- can be inhibitory or excitatory (mostly excitatory) and is involved in muscle contraction (recall curare), memory, and REM sleep.
Serotonin- is a mood enhancer, but affects mood by calming rather than stimulating. Depression drugs inhibit the reuptake of serotonin thus increasing it’s effect.
Dopamine - two major roles are to control conscious motor activity and enhance pleasurable feelings in the brain’s reward system (anticipated reward).
Norepinephrine/Noradrenalin- involved in arousal during fight-or-flight response.
Epinephrine/Adrenaline- involved in stress response (fight-or-flight response).
Amino Acids
GABA: always carry inhibitory messages
Aspartate: always carry excitatory messages
Glycine: always carry inhibitory messages
Glutamate: always carry excitatory messages
After synapses the neurotransmitters clear the area by:
3.Still other molecules diffuse out of the cleft and are carried away as waste material by the cerebrospinal fluid
2.The enzymes present in the synaptic cleft destroy some neurotransmitter molecules
1.Reuptake channels, the axon terminal of the cell reabsorbs many neurotransmitter molecules; the axon then recycles them to be used again
Synapses is the release of one or more neurotransmitter.
The postsynaptic cell has receptors on he dendrites to receive the neurotransmitter. The receptor never directly touches the other cell. There is a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft, which the neurotransmitters travel across.
Neurons communicate when two neurons connect with one another
When one cells axon connects with another cells's dendrites they create a connection called a synapse or synaptic connection
The more these neurons connect with eachother, the stronger the synaptic connection becomes. This creates strong neaural pathway
Structure of a neuron
The axons are the senders that send out information to the other cells and is covered in a thick tissue called myelin sheath.
Sender
The dendrites are the receivers that act as receptors for signals travelling from other neurons, carrying information toward the main body of the nerve cell.
Recievers
The soma is the body of the nerve cell
Information holder
History of the Brain
Abnormalities and Traumas
Key Case Studies
1953: Brenda Milner
1848: Phineas Gage
He was an American railroad construction foreman remembered for his improbable survival of an accident in which a large iron rod was driven completely through his head, destroying much of his brain's left frontal lobe.
Early Physician experiments
1934
Egas Moniz carries out the first lobotomy operation. He also invented angiogrpahy: a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers.
1929
EEG was invented by Hans Berger
EEG is is a test used to find problems related to electrical activity of the brain. An EEG tracks and records brain wave patterns
1664
Thomas Willis publishes the first brain atlas. This is considered the birth of neaurscience
1500
Shortly after the ban on dissestion; Leonardo Di Vinci fashioned a wax cast of an ox brain after many disections of the human and animal brain
170 BCE
Roman physician Galen disected monkeys and pig brains, he believed that spirts throughout the body were housed in the brain
Ancient History
335 BCE Aristotle
Thought the brain was a hot and cool radiator for the body
387 BCE Plato
460 BCE Hippocrates
Father of modern medicine
Thought the brain told what us to do
2500 BCE Trenpancition
Created holes in the skull to remove the "idiot stone"
1700 Egyptian mummification practices
During this era they pulled out the brain through the nose; piece by piece they took it out with a hook
History of the brain
The brain has evolved over the past
few million years, it has chronologically
grew starting with:
3. Neo Cortex
2. Limbic System
1. Hind Brain