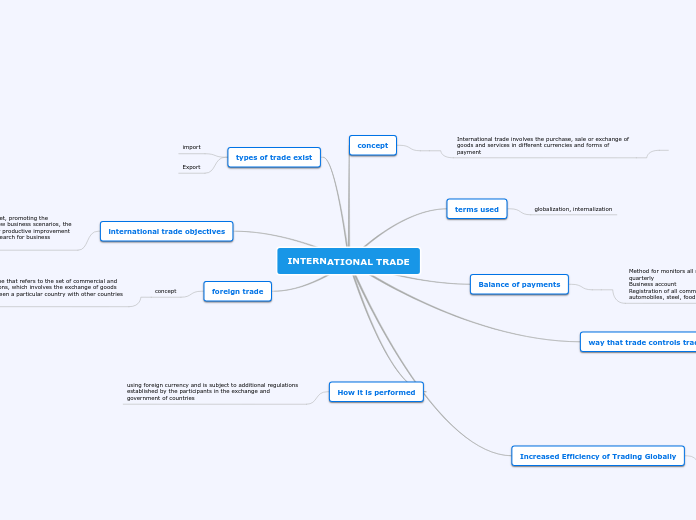
Big Ideas
Grade 10: 1. Plants and animals, including humans, are made of specialized cells, tissues, and organs that are organized into systems.
2. Developments in medicine and medical technology can have social and ethical implications.
Grade 11: Plants: Anatomy, Growth, and Function
1. Plants have specialized structures with distinct functions that enable them to respond and adapt to their environment.
2. Plant variety is critical to the survival and sustainability of ecosystems.
Grade 11: Animals: Structure and Function
1. Groups of organs with specific structures and functions work together as systems, which interact with other systems in the body.
2. The development and uses of technology to maintain human health are based, in part, on the changing needs of society.
Grade 12: Homeostasis
1. Organisms have strict limits on the internal conditions that they can tolerate.
2. Systems that maintain homeostasis rely on feedback mechanisms.
3. Environmental factors can affect homeostasis.
Grade 12: Metabolic Processes
1. All metabolic processes involve chemical changes and energy conversions.
2. An understanding of metabolic processes enables people to make informed choices with respect to a range of personal, societal, and environmental issues.
Grade 12: Biochemistry
1. Technological applications that affect biological processes and cellular functions are
used in the food, pharmaceutical, and medical industries.
2. Biological molecules and their chemical properties affect cellular processes and biochemical reactions.
3. Biochemical compounds play important structural and functional roles in cells of all living organisms.
Grade 11: Genetic Processes
1. Genetic and genomic research can have social and environmental implications.
2. Variability and diversity of living organisms result from the distribution of genetic materials during the process of meiosis.
Grade 12: Molecular Genetics
1. DNA contains all the genetic information for any living organism.
2. Proteins control a wide variety of cellular processes.
3. Genetic research and biotechnology have social, legal, and ethical implications.
Grade 9: 1. Ecosystems are dynamic and have the ability to respond to change, within limits, while
maintaining their ecological balance.
2. People have the responsibility to regulate their impact on the sustainability of ecosystems in order to preserve them for future generations.
Grade 11: Evolution
1. Evolution is the process of biological change over time based on the relationships
between species and their environments.
2. The theory of evolution is a scientific explanation based on a large accumulation of evidence.
3. Technology that enables humans to manipulate the development of species has economic and environmental implications.
Grade 11: Diversity of Living Things
1. All living things can be classified according to their anatomical and physiological
characteristics.
2. Human activities affect the diversity of living things in ecosystems.
Grade 12: Population Dynamics
1. Population growth follows predictable patterns.
2. The increased consumption of resources and production of waste associated with population growth result in specifc stresses that affect Earth’s sustainability.
3. Technological developments can contribute to or help offset the ecological footprint associated with population growth and the consumption of natural resources.
Biology Overall Expectations
Overall Expectation 3: Basic Concepts
Grade 10 - demonstrate an understanding of the hierarchical organization of cells, from tissues, to organs, to systems in animals and plants.
Grade 11: Plants: Anatomy, Growth, and Function - F3. demonstrate an understanding of the diversity of vascular plants, including their structures, internal transport systems, and their role in maintaining biodiversity.
Grade 11: Animals: Structure and Function - E3. demonstrate an understanding of animal anatomy and physiology, and describe disorders of the respiratory, circulatory, and digestive systems.
Grade 12 - Homeostasis: E3. demonstrate an understanding of the anatomy and physiology of human body systems, and
explain the mechanisms that enable the body to maintain homeostasis.
Grade 12 - Metabolic Processes: C3. demonstrate an understanding of the chemical changes and energy conversions that occur in metabolic processes.
Grade 12 - Biochemistry: B3. demonstrate an understanding of the structures and functions of biological molecules, and the biochemical reactions required to maintain normal cellular function.
Grade 11 - Genetic Processes: D3. demonstrate an understanding of concepts, processes, and technologies related to the transmission of hereditary characteristics
Grade 12 - Molecular Genetics: D3. demonstrate an understanding of concepts related to molecular genetics, and how genetic modification is applied in industry and agriculture.
Grade 9 - demonstrate an understanding of the dynamic nature of ecosystems, particularly in terms of ecological balance and the impact of human activity on the sustainability of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
Grade 11 - Evolution: C3. demonstrate an understanding of the theory of evolution, the evidence that supports it, and some of the mechanisms by which it occurs.
Grade 11 - Diversity of Living Things: B3. demonstrate an understanding of the diversity of living organisms in terms of the principles of taxonomy and phylogeny
Grade 12 - Population Dynamics: F3. demonstrate an understanding of concepts related to population growth, and explain the factors that affect the growth of various populations of species.
Overall Expectation 2: Inquiry
Grade 10 - investigate cell division, cell specialization, organs, and systems in animals and plants, using research and inquiry skills, including various laboratory techniques;
Grade 11 - Plants: Anatomy, Growth, and Function: F2. investigate the structures and functions of plant tissues, and factors affecting plant growth;
Grade 11 - Animals: Structure and Function: E2. investigate, through laboratory inquiry or computer simulation, the functional responses of the respiratory and circulatory systems of animals, and the relationships between their respiratory, circulatory, and digestive systems;
Grade 12 - Homeostasis: E2. investigate the feedback mechanisms that maintain homeostasis in living organisms;
Grade 12 - Metabolic Processes: C2. investigate the products of metabolic processes such as cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
Grade 12 - Biochemistry: B2. investigate the chemical structures, functions, and chemical properties of biological molecules involved in some common cellular processes and biochemical reactions;
Grade 11 - Genetic Processes: D2. investigate genetic processes, including those that occur during meiosis, and analyse data to solve basic genetics problems involving monohybrid and dihybrid crosses;
Grade 12 - Molecular Genetics: D2. investigate, through laboratory activities, the structures of cell components and their roles in
processes that occur within the cell;
Grade 9 - investigate factors related to human activity that affect terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, and explain how they affect the sustainability of these ecosystems;
Grade 11 - Evolution: C2. investigate evolutionary processes, and analyse scientific evidence that supports the theory of evolution;
Grade 11 - Diversity of Living Things: B2. investigate, through laboratory and/or field activities or through simulations, the principles of scientific classification, using appropriate sampling and classification techniques;
Grade 12 - Population Dynamics: F2. investigate the characteristics of population growth, and use models to calculate the growth of populations within an ecosystem;
Overall Expectation 1: STSE
Grade 10 - evaluate the importance of medical and other technological developments related to systems biology, and analyse their societal and ethical implications;
Grade 11: Plants: Anatomy, Growth, and Function - F1. evaluate the importance of sustainable use of plants to Canadian society and other cultures;
Grade 11 - Animals: Structure and Function: E1. analyse the relationships between changing societal needs, technological advances, and our understanding of internal systems of humans;
Grade 12 - Homeostasis: E1. evaluate the impact on the human body of selected chemical substances and of environmental
factors related to human activity;
Grade 12 - Metabolic Processes: C1. analyse the role of metabolic processes in the functioning of biotic and abiotic systems, and evaluate the importance of an understanding of these processes and related technologies to personal choices made in everyday life;
Grade 12 - Biochemistry: B1. analyse technological applications of enzymes in some industrial processes, and evaluate
technological advances in the feld of cellular biology;
Grade 11 - Genetic Processes: D1. evaluate the importance of some recent contributions to our knowledge of genetic processes, and analyse social and ethical implications of genetic and genomic research;
Grade 12 - Molecular Genetics: D1. analyse some of the social, ethical, and legal issues associated with genetic research and biotechnology;
Grade 9 - assess the impact of human activities on the sustainability of terrestrial and/or aquatic ecosystems, and evaluate the effectiveness of courses of action intended to remedy or mitigate negative impacts
Grade 11 - Evolution: C1. analyse the economic and environmental advantages and disadvantages of an artificial selection technology, and evaluate the impact of environmental changes on natural selection and endangered species;
Grade 11 - Diversity of Living Things: 1. analyse the effects of various human activities on the diversity of living things;
Grade 12 - Population Dynamics: F1. analyse the relationships between population growth, personal consumption, technological development, and our ecological footprint, and assess the effectiveness of some Canadian initiatives intended to assist expanding populations;