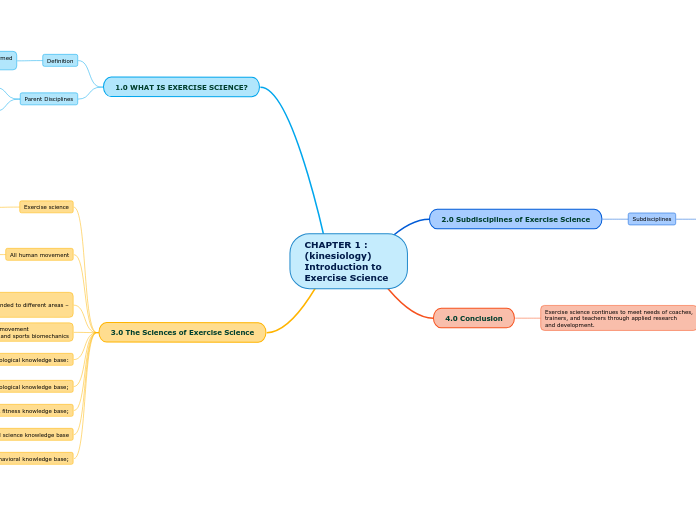
CHAPTER 1 : (kinesiology)
Introduction to Exercise Science
3.0 The Sciences of Exercise Science
Behavioral knowledge base;
1. Motor behavior
2. Exercise and sport psychology
Social science knowledge base
1. Sport sociology
2. Sport history
Health & fitness knowledge base;
1. Clinical exercise physiology
2. Physical activity
Physiological knowledge base;
1. Exercise physiology
2. Sport nutrition
Sport medicine & kinesiological knowledge base:
1. Athletic training
2. Sport biomechanics
3. Clinical biomechanics
Exercise science study movement
* clinical biomechanics and sports biomechanics
Subdisciplines overlap
* exercise physiology expanded to different areas –
sports nutrition
All human movement
Many branches of science can be applied to
exercise - biology, chemistry physics and
psychology
Biology and chemistry
exercise physiology
Physics
expanding the mechanics of movement –
biomechanics.
Psychology
development of motor behavior and
exercise and sports psychology
Exercise science
refers to the application of science to the
phenomenon of exercise
1.0 WHAT IS EXERCISE SCIENCE?
Parent Disciplines
Attempts to describe, study and expand its body of
knowledge.
For example: biology, chemistry, physics and
psychology, physiology, mathematics, engineering
Definition
The scientific study of human movement performed
to maintain or improve physical fitness.
4.0 Conclusion
Exercise science continues to meet needs of coaches,
trainers, and teachers through applied research
and development.
2.0 Subdisciplines of Exercise Science
Subdisciplines
the science components of exercise
science within which the body of knowledge is
describes, studied and expanded.
1. Exercise physiology and Biochemistry
2. Biomechanics
3. Motor Learning and Control
4. Sports Medicine
5. Exercise and Sport Psychology