Research methodology
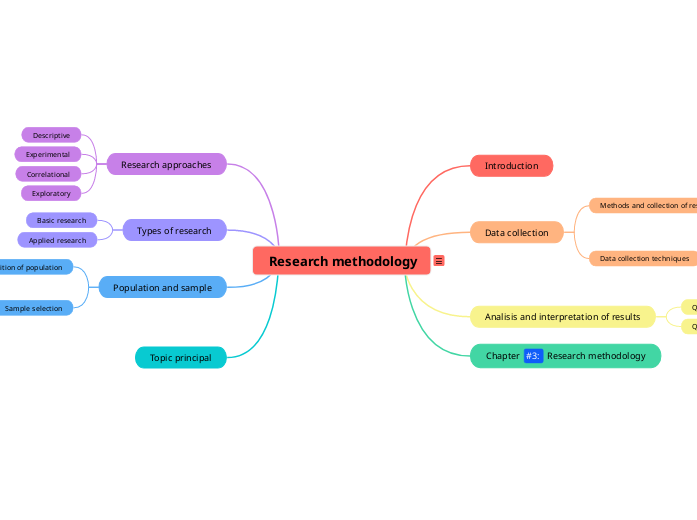
Chapter #3: Research Methodology
Chapter 3 of a research study focuses on the research methodology, which outlines the systematic approach taken to gather and analyze data. This chapter is crucial as it provides a roadmap for how the research will be conducted.
Data Collection
Data collection is a fundamental aspect of research methodology. It involves selecting appropriate methods and techniques to gather information. Common methods include qualitative approaches, such as interviews and focus groups, and quantitative approaches, such as surveys and experiments. Techniques may vary from structured questionnaires to observational studies, depending on the research objectives.
Research Instruments
Research instruments are the tools used to collect data. These can include questionnaires, checklists, and scales designed to measure specific variables. The choice of instrument is critical, as it must be valid and reliable to ensure accurate data collection.
Analysis and Interpretation of Results
Once data is collected, it undergoes analysis and interpretation. This involves applying statistical methods for quantitative data or thematic analysis for qualitative data. The goal is to draw meaningful conclusions from the data, contextualizing findings within the broader research framework.
Research Approaches
Research approaches can be categorized into several types, including descriptive, experimental, correlational, and exploratory. Each approach serves different purposes and is chosen based on the research questions and objectives.
Types of Research
Research can be classified into basic and applied research. Basic research seeks to expand knowledge without immediate practical application, while applied research aims to solve specific problems or address practical issues.
Population and Sample
Understanding the population and sample is essential for research validity. The population refers to the entire group of individuals relevant to the study, while a sample is a subset selected for data collection. Sampling techniques, such as random, stratified, or convenience sampling, determine how participants are chosen, impacting the generalizability of the results.
Topic principal
Population and sample
Sample selection
Convenience sampling
Stratified sampling
Random sampling
Definition of population
Types of research
Applied research
Basic research
Research approaches
Exploratory
Correlational
Experimental
Descriptive
Chapter #3: Research methodology
Analisis and interpretation of results
Qualitative data analysis methods
Quantitative data analysis methods
Data collection
Data collection techniques
Measuring scale
Checklist
Questionnaires
Methods and collection of results
Quantitative approach
Qualitative approach
Introduction