door Hanis Haziqah 3 jaren geleden
192
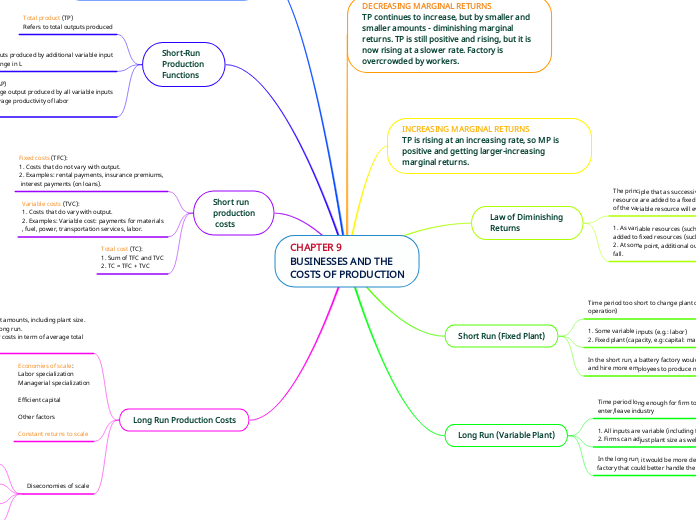
CHAPTER 9 BUSINESSES AND THE COSTS OF PRODUCTION
The short run in production costs involves both fixed costs, which do not change with output levels, and variable costs, which do vary with output. Total cost is the sum of fixed and variable costs.