Turning effect of forces
Definition of the Moment of a Force
Moment of a Force= F x d
Definition: The moment of a force(M) about a point or pivot(O) is the product of the force(F) and the perpendicular distance(d) from the line of action of the fprce to the point/pivot.
Stability and CG
Neutral equilibrium
when a body remanis wherever it is displaced
Unstable equilibrium
when a body continues to move away from its original position after it is being slightly displaced
Stable equilibrium
when a body is able to return to its original position after being displaced slightly
Principle of Moments
When a body is in equilibrium, the sum of clockwise moments about the balance point or pivot = to the sum of anti-clokwise moments about the same point
Total clockwise moments about the same point = total anti-clockwise moments about a point
Moment
The turning effect(or moment) of a force depends on
b) Perpendicular distance between the point of the application of the force and the pivot
a) Magnitude of the force
Definition: The moment of a force is the turning effect of a force about a point
Centre of Gravity(CG)
Centre of gravity of a regular-shaped object
E.g metre rule. The centre of gravity is its centre(or geometrical centre)
Centre of gravity of a irregular-shaped object
centre of gravity is always vertically below the pivot(point of suspension) when it is hanging freely about it
Definition: The centre of gravity(CG) of a body is that point where the whole weight of the body seems to act
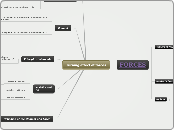
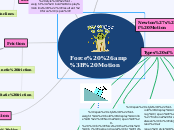
FORCES
friction
contact force
always act in an opposite direction to the force applied on an object
Newton's law of motion
3rd law of motion
action-reaction forces
occurs when 2 forces are present
2nd law of motion
unbalanced forces
Net F=ma
1st law of motion
balanced forces
Body continues to move at constant spped in a straight line unless an unbalanced force acts on it.
effects of forces
stop a moving object
move a stationary object
change the shape of an object
change the direction of an object
Decelerates an object
Accelerates an object