https://www.elsevier.es/es-revista-revista-medica-clinica-las-condes-202-articulo-enfermedades-del-tejido-conectivo-importancia-S0716864012703309
revisado presentacion Morfofiisiologia I docente A. BULA CALDERON.
Bibliografia: López, P., & Casasbuenas, J. (2018). La biopsia y la citología, pilares del
diagnóstico médico. Revista Médica Sanitas, 29–38.
http://www.unisanitas.edu.co/Revista/54/LA_BIOPSIA_Y_LA_CITOLOGI
A_PILARES.pdf
PARASINPATICO
SIMPATICO
CRANEALES (12)
ESPINALES (31)
AUTONOMO
SOMATICO
NERVIOSO
SNC
ENCEFALO
MEDULA ESPINAL
CEREBRO. CEREBELO. TRONCO ENCEFALICO.
MESENCÉFALO PROTUBERANCIA. BULBO RAQUIDEO.
Tejido Hematopoyético: medula ósea roja; Medula ósea Amarilla. Se encuentra en la cavidad medular de los huesos largos y en
las celdillas del hueso esponjoso.
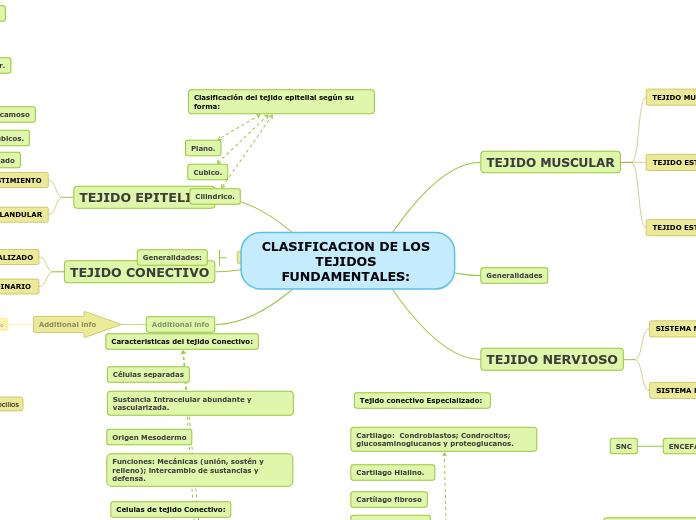
Cartílago Elástico
Cartílago fibroso
Cartilago Hialino.
Cartilago: Condroblastos; Condrocitos; glucosaminoglucanos y proteoglucanos.
Tejido conectivo Especializado:
Células Migrantes: (moviles o transitorias) glóbulos Blancos (Neutrofilos, eosinofilos, etc)
Células fijas: Fibroblastos ; pericitos y Adipositos.
Celulas de tejido Conectivo:
Funciones: Mecánicas (unión, sostén y relleno); intercambio de sustancias y defensa.
Origen Mesodermo
Sustancia Intracelular abundante y vascularizada.
Células separadas
Caracteristicas del tejido Conectivo:
Seudoestratificado
Estratificado Cubicos.
Estratificado escamoso
Transicional.
Simple Columnar.
simple cubico
simple escamoso
Clasificación por Estratos celulares:
Cilindrico.
Cubico.
Plano.
Clasificación del tejido epitelial según su forma:
lamina reticular
lamina Basal
Uniones comunicantes
uniones anclantes
Uniones oclusivas
membrana lateral
membrana basal
Membrana Apical
microvellosidades.
Estereocilios
Tienen una polaridad definida por su orientación espacial:
Generalidades:
son tejidos avasculares
Se Caracterizan:
unidas por complejos de unión
poca matriz extracelular.
poco espacio intracelular
disposición organizada.
celulas estrechamente unidas.
CLASIFICACION DE LOS TEJIDOS FUNDAMENTALES:
Global warming is the ongoing rise of the average temperature of the Earth's climate system which has various negative effects.
Additional info
TEJIDO CONECTIVO
Overpopulation creates an increased demand for energy as well as having negative effects on our environment and ecosystems.
ORDINARIO
Over-cultivation is the practice of excessive farming on a piece of land to the point of degradation of the soil as well as the land itself.
ESPECIALIZADO
Water is essential for agricultural production and food security. It is the lifeblood of ecosystems, including forests, lakes, and wetlands.
Overpopulation affects our water and this has negative outcomes.
MEDULA OSEA
ADIPOSO
CARTILAGO
HUESO
SANGRE
TEJIDO EPITELIAL
Climate change is likely to both increase electricity demand for cooling in the summer and decrease electricity, natural gas, heating oil, and wood demand for heating in the winter.
TEJIDO GLANDULAR
How will climate change affect the production of clean energy?
e.g.: solar, wind, water
ENDOCRINO
EXOCRINO
TEJIDO DE REVESTIMIENTO
New infrastructure investments may be necessary to meet increased energy demand.
e.g.: nuclear power plants
TEJIDO NERVIOSO
Healthy ecosystems and rich biodiversity are fundamental to life on our planet.
Even small changes in average temperatures can have a significant effect upon ecosystems.
SISTEMA NERVIOSO PERISFERICO
Climate change will affect mountain and lowland ecosystems, the diversity of wildlife, and the distribution of freshwater.
e.g.: forest fires
está formado porreceptores sensoriales y nervios (sensitivos y motores) que actúan como líneas de comunicación hacia y desde el sistema nervioso central.
SISTEMA NERVIOSO CENTRAL
Climate change is affecting the habitats of several species, which must either adapt or migrate to areas with more favorable conditions.
e.g.: natural habitat disappearing
La neurona es la Unidad estructural y funcional del tejido
nervioso.
El Sistema Nervioso Central actúa como centro de
control y elaboración de respuestas frente a
estímulos del medio externo e interno
Generalidades
TEJIDO MUSCULAR
Climate change is supported by scientific evidence.
TEJIDO ESTRIADO CARDIACO
Write down the consequences caused by this issue and how it will affect our lives and the environment in the future.
e.g.: flooding, rainfall increase
Fibras musculares: compuestas por
células que se ramifican.
Son de características unicelulares; forman sarcomeras (actinass, mioscinas) tienen forma de "Y"
TEJIDO ESTRIADO ESQUELETICO
Write down the consequences caused by the melting of the ice-caps and how it will affect our lives and the environment in the future.
e.g.: decreasing of polar bear habitat
Conformadas por fibras blancas, fibras rojas e intermedias.
Son multinucleados; los núcleos se ubican hacia la periferia
TEJIDO MUSCULAR LISO
Write down the consequences caused by this issue and how it will affect our lives and the environment in the future.
e.g.: decreasing of land surface
Células ahusadas Núcleo central, ovalado, eucromático Citoplasma eosinófilo, homogéneo sin estriaciones.
No es tejido organizado, no forman sarcomeras esta presente en vasos sanguineos, visceras.