Coming Together
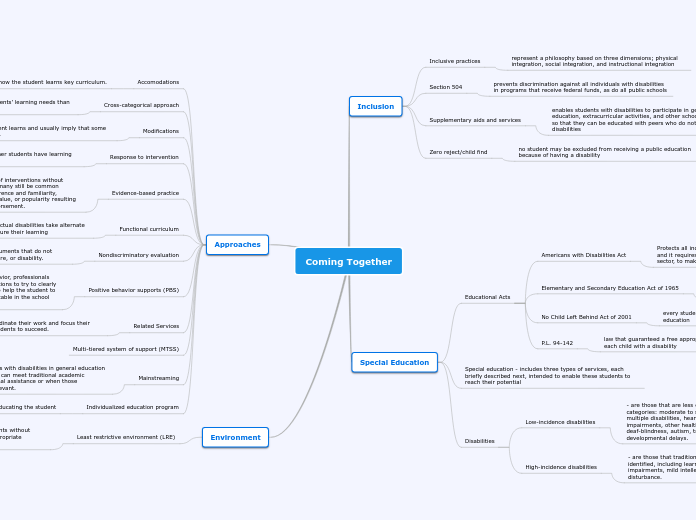
Environment
Least restrictive environment (LRE)
an educational setting most like that for students without disabilities in which they can succeed with appropriate supports provided
Approaches
Individualized education program
a sort of roadmap for educating the student
Mainstreaming
involves placing students with disabilities in general education settings only when they can meet traditional academic expectations with minimal assistance or when those expectations are not relevant.
Multi-tiered system of support (MTSS)
Related Services
enables educators to coordinate their work and focus their efforts to help all their students to succeed.
Positive behavior supports (PBS)
when a student displays problematic behavior, professionals implement increasingly intensive interventions to try to clearly identify the reason for the behavior and to help the student to learn alternative behaviors that are acceptable in the school setting.
Nondiscriminatory evaluation
students must be assessed using instruments that do not discriminate on the basis of race, culture, or disability.
Functional curriculum
students with significant intellectual disabilities take alternate assessments designed to measure their learning
Evidence-based practice
Is designed to eliminate the use of interventions without demonstrated effectiveness that many still be common practice because of teacher preference and familiarity, tradition, anecdotes about their value, or popularity resulting from advertising or celebrity endorsement.
Response to intervention
is an approach for exploring whether students have learning disabilities.
Modifications
refer to what the student learns and usually imply that some curriculum is removed.
Cross-categorical approach
where more attention is paid to students’ learning needs than to their labels
Accomodations
changes in how the student learns key curriculum.
Special Education
Disabilities
High-incidence disabilities
- are those that traditionally have been most commonly identified, including learning disabilities, speech or language impairments, mild intellectual disabilities, and emotional disturbance.
Low-incidence disabilities
- are those that are less common and include all the other categories: moderate to severe intellectual disabilities, multiple disabilities, hearing impairments, orthopedic impairments, other health impairments, visual impairments, deaf-blindness, autism, traumatic brain injury, and developmental delays.
Special education - includes three types of services, each briefly described next, intended to enable these students to reach their potential
Educational Acts
P.L. 94-142
law that guaranteed a free appropriate public education to each child with a disability
No Child Left Behind Act of 2001
every student with or without a disability can have an education
Elementary and Secondary Education Act of 1965
it is the law that has the goal of ensuring that all students, including those who live in poverty, have equal access to a high quality education
Americans with Disabilities Act
Protects all individuals with disabilities from discrimination, and it requires most employers, whether in a public or private sector, to make reasonable accommodations for them
Inclusion
Zero reject/child find
no student may be excluded from receiving a public education because of having a disability
Supplementary aids and services
enables students with disabilities to participate in general education, extracurricular activities, and other school settings so that they can be educated with peers who do not have disabilities
Section 504
prevents discrimination against all individuals with disabilities in programs that receive federal funds, as do all public schools
Inclusive practices
represent a philosophy based on three dimensions; physical integration, social integration, and instructional integration