door Tinkuy Travel 10 maanden geleden
82
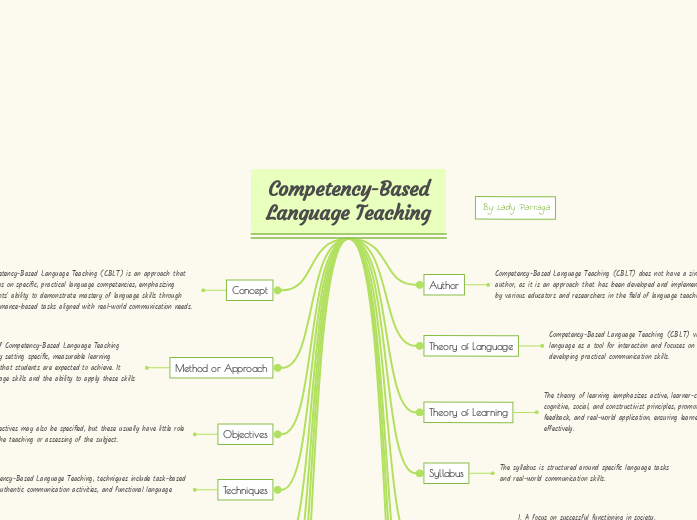
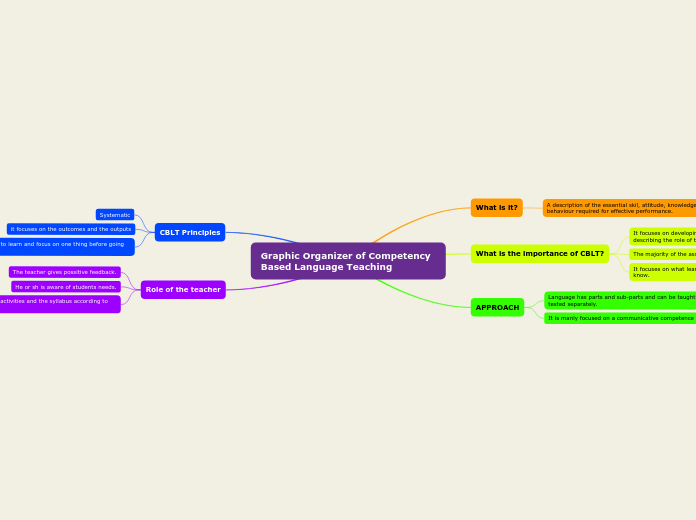
Competency-Based Language Teaching
Competency-Based Language Teaching (CBLT) emphasizes the mastery of practical language skills through performance-based tasks aligned with real-world communication needs. It views language as a tool for interaction and focuses on developing practical communication competencies.