door yasmeen riad 3 jaren geleden
537
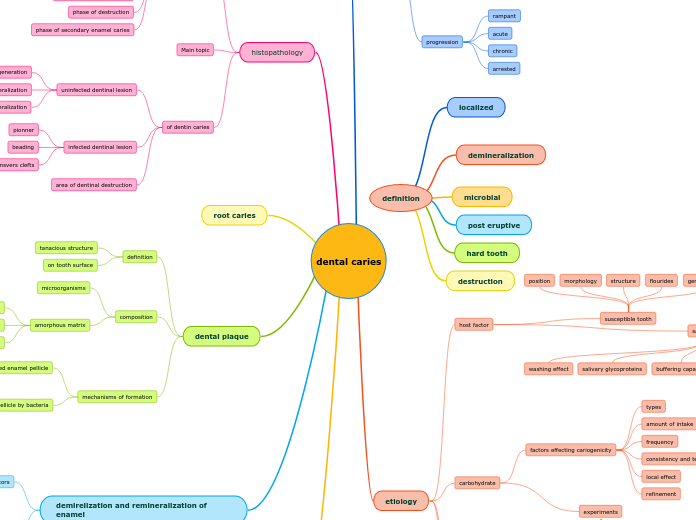
dental caries
The development of dental caries involves a complex interplay of various factors, including the composition and presence of dental plaque, which is a tenacious structure on the tooth surface.
door yasmeen riad 3 jaren geleden
537

Meer zoals dit
mature community
intermediate community
pioneer community
inorganic content
protein
liquefaction foci transvers clefts
beading
pionner
zone of hypermineralization
zone of hypomineralization
zone of fatty degeneration
surface zone
body of the lesion
dark zone
translucent zone
firm adhesion to tooth surfaces
synthesis of intracellular storage polysaccharides
actively transport
synthesis of extracellular polysaccharides
aciduric
acidogenic
orlands
millers
hopewood house
vipeholm
turku study
refinement
local effect
consistency and texture
frequency
amount of intake
supply of ions remineralization
antimicrobial effect
buffering capacity
salivary glycoproteins
washing effect
genetic effects
flourides
structure
morphology
position