door Alex Lee 5 jaren geleden
315
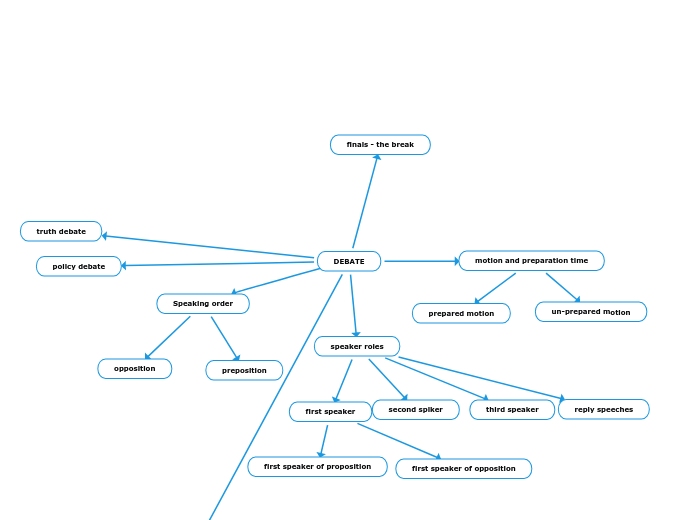
Dynamics Mindmap Alex K, Alex L, Kusha S, Yasaman P
This content discusses various fundamental principles of classical mechanics, focusing on the different types of forces and their roles in motion. It delves into Newton's three laws of motion, explaining how they govern the behavior of objects.