Elementary Mathematics
(MTE 280 Fall 2019)
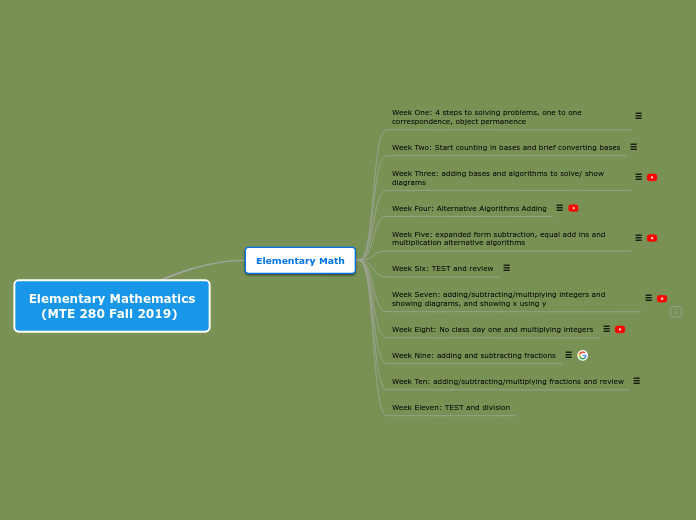
Elementary Math
Week Eleven: TEST and division
Week Ten: adding/subtracting/multiplying fractions and review
adding fractions uses 3 rectangles
- one per fraction and then one for the answer
subtracting fractions uses two rectangles
- one to show both fractions and the other to show the answer
multiplying fractions takes one rectangle
- count only the sections in where they meet
Week Nine: adding and subtracting fractions
what does the numerator and denominator mean?
Numerator: number of pieces we have
Denominator: how big a piece is going to be
anchor fraction: fraction we know that helps us figure out other fractions
*never put a fraction over 1*
Week Eight: No class day one and multiplying integers
if the first number is negative then you need a zero bank
rules:
1) if the signs are the same: +
2) if the signs are different: -
2(-3): two groups of 3 negatives
-3(-1): take away 3 groups of 1 negative
Week Seven: adding/subtracting/multiplying integers and showing diagrams, and showing x using y
always need ENOUGH two sided counters when trying to add pairs to make a certain number
a zero pair is when a positive and a negative cancel each other out
a zero bank is when you have multiple zero pairs (as many as needed)
show -5 using 9: ++-------
74(++) + -38(-)= 36
- since 74 is a bigger positive number it gets two signs and since 38 is negative and smaller it gets one sign. since they are opposite they subtract and the answer will be positive
Week Six: TEST and review
going to have to figure out how to add a document because I was trying to upload my review pages as a reference and it was not letting me do so
Week Five: expanded form subtraction, equal add ins and multiplication alternative algorithms
Lattice multiplication (video)
Equal add ins: Adding the same thing to both numbers to make it easier to subtract
27-14 (add 3 to both) 30-17= 13
55-38 (add 2) 57-40= 17
expanded:
48-15= 40+8 - 10+5= 33
friendly numbers:
37+28= 35+30= 65
Array: separated sporadic
Area Model (video)
Week Four: Alternative Algorithms Adding
Left to right:
358+296= 500+140+14= 654
Trading off:
8+5= 10+3= 13
7+9= 6+10= 16
Scratch:
count in the bases and when you reach the number that your base is, put a slash through the number. then you'll continue adding and count up all the slashes (hard to explain and it make sense since I know what I'm doing so I have to figure out how to add pictures because it won't let me)
Week Three: adding bases and algorithms to solve/ show diagrams
Convert to base 10:
43 seven --> llll... = 31
Solving base 10 conversions:
4312six --> 4(6^3)+3(6^2)+1(6^1)+2(6^0)
LLLLLeaving base 10:
stranger things division
8 l__37___ = 45eight
4 l 5
l
Week Two: Start counting in bases and brief converting bases
14 nine --> ............. = 13
23 seven --> ................. = 17
16 eight --> .............. = 14
When no base is written, it is considered to be base 10
Convert 23 to base seven --> lll.. = 32seven
convert 43 to base 5 --> ◼️lll... = 133five
🔳 = cube
◼️ = flat
l = long
. = unit
Week One: 4 steps to solving problems, one to one correspondence, object permanence
Four steps to solving problems:
- Understand what the problem is
- Develop a solution
- Carry out a solution
- Look back to see if it was right
One to one correspondence: know how to count and then classifying an object as one
Object permanence: knowing how many objects are there without having to recount