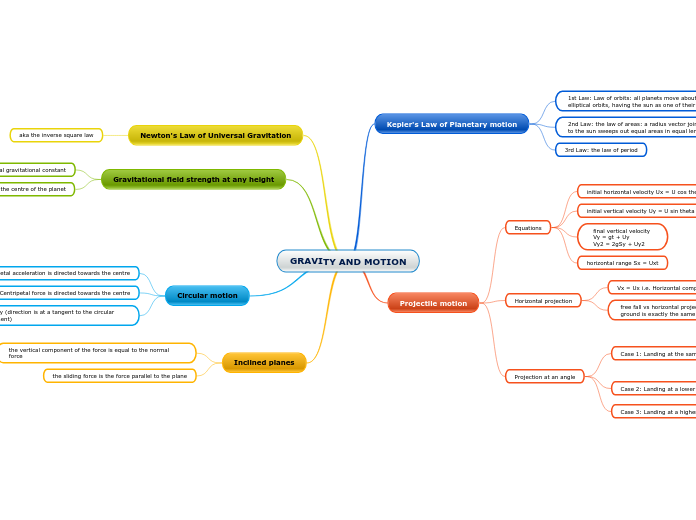
GRAVITY AND MOTION
Inclined planes
the sliding force is the force parallel to the plane
the vertical component of the force is equal to the normal force
Circular motion
Tangential velocity (direction is at a tangent to the circular path at that moment)
Centripetal force is directed towards the centre
Centripetal acceleration is directed towards the centre
Gravitational field strength at any height
*r is measured from the centre of the planet
G is the universal gravitational constant
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation
aka the inverse square law
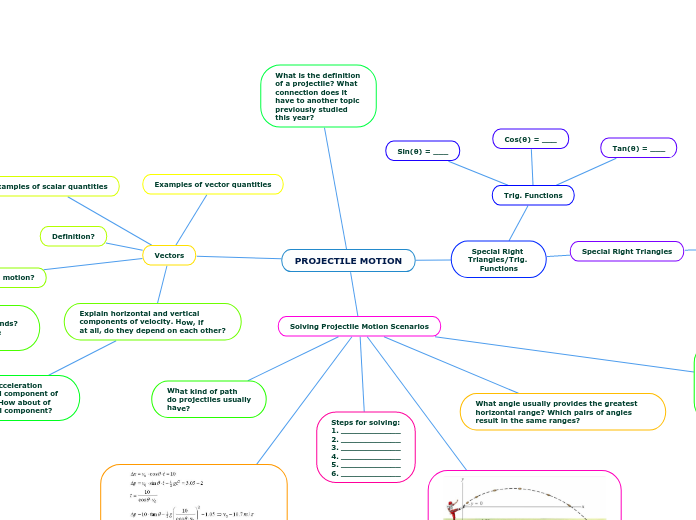
Projectile motion
Projection at an angle
Case 3: Landing at a higher height than launch e.g. basketball
Sy is some positive quantity
i.e. Sy =3.1 - 1.6 = +1.5m
Case 2: Landing at a lower height than launch
Sy is some -ve quantity
Case 1: Landing at the same height as at launch
Total hang time is twice the time taken to reach max ht
Sy = 0
impact velocity is the same as the initial (launch) velocity
Horizontal projection
free fall vs horizontal projection: time taken to reach the ground is exactly the same
Vx = Ux i.e. Horizontal component of the velocity is constant
Vx=Ux
Equations
horizontal range Sx = Uxt
final vertical velocity
Vy = gt + Uy
Vy2 = 2gSy + Uy2
initial vertical velocity Uy = U sin theta
initial horizontal velocity Ux = U cos theta
Kepler's Law of Planetary motion
3rd Law: the law of period
2nd Law: the law of areas: a radius vector joining any planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal lengths of time
1st Law: Law of orbits: all planets move about the sun in elliptical orbits, having the sun as one of their foci