Price P, Substitute Ps, Comp Pc, Income y, Taste t, Advertising A, Population pop
Increase in Demand shifts curve to the RIGHT, decrease = LEFT
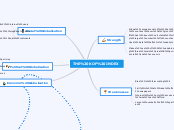
Protectionism aims to restrict and limit free trade with countries to protect home producers from foreign suppliers
Over dependence on specific output, undermine local culture, dumping.
Free Trade V Protectionism
Free Trade
reduces conflict, encourages efficient production & entrepreneurship, greater choice for consumers, creates unemployment
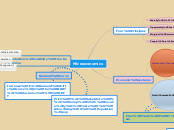
Microeconomics
Demand Curve
Production Possibility Frontier/Curve
Going point to point = opportunity costs
All points outside the curve are unattainable
All points ON the curve are efficient
Economic systems
Free market economy
Low government interference US/EU
Cons = can be socially irresponsible, private wealth at expense of others
benefits = self interest, prices & market, private property
Command economy
Government decides price of produce = communist government
cons = lack of individual freedom, risk of exploitation of workers
benefits = social solidarity, great security for people
Four Principles
People are rational
Marginal Decision
Opportunity Cost
Scarcity L, Lb, K