door Christopher Tabet 1 jaar geleden
189
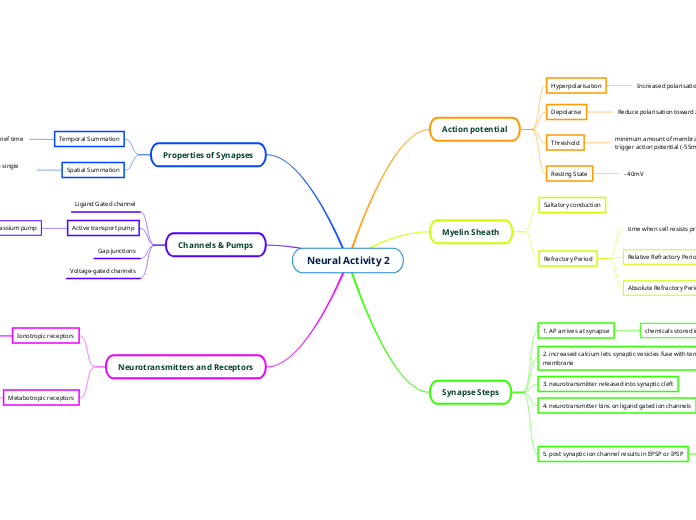
Neural Activity 2
Neural activity involves a complex interplay of synaptic steps, beginning with the arrival of an action potential at the synapse, triggering the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft.