Glomerular disease
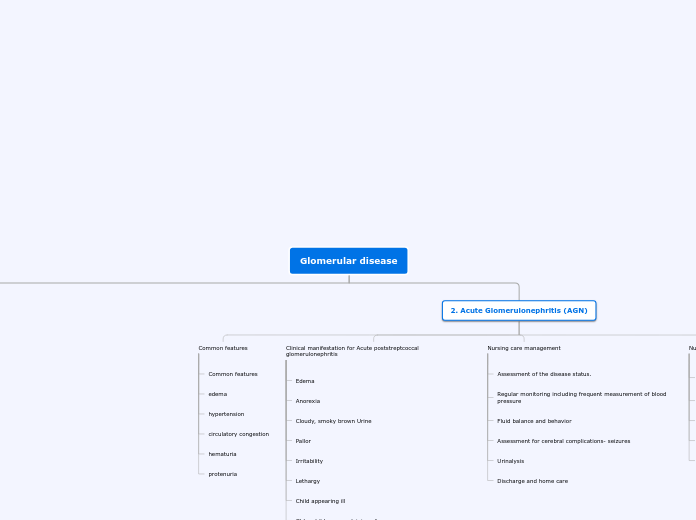
2. Acute Glomerulonephritis (AGN)
Nursing Diagnosis
- Coping Ineffective : Individual
- Risk for Infection
- Risk for Injury
- Fluid Volume Excess related to edema
Imbalanced Nutrition less than body requirements
related to restricted diet
Discharge and home care
Urinalysis
Assessment for cerebral complications- seizures
Fluid balance and behavior
Regular monitoring including frequent measurement of blood pressure
Assessment of the disease status.
Clinical manifestation for Acute poststreptcoccal glomerulonephritis
Older children complaining of
Mild to moderately elevated blood pressure.
Vomiting possible
dysuria
abdominal discomfort
headaches
Child appearing ill
Lethargy
Pallor
Cloudy, smoky brown Urine
Anorexia
Common features
protenuria
hematuria
circulatory congestion
hypertension
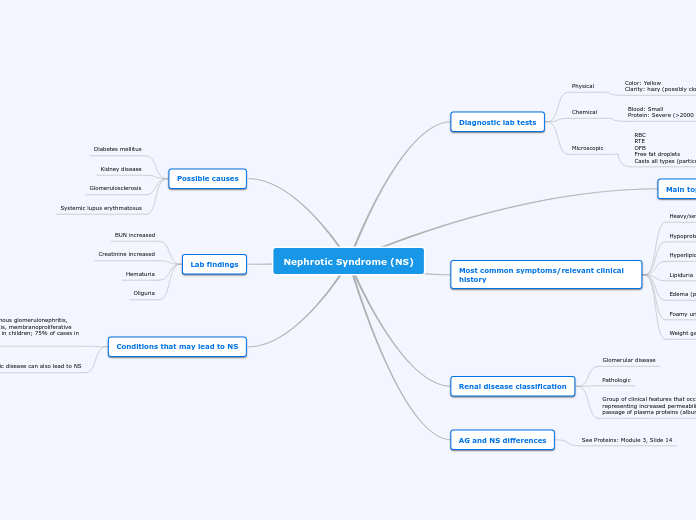
Nephrotic syndrome:
Nursing care management
Strict intake and output record
Monitor daily weight and abdominal girth.
Assess for edema
Detect any early signs of complications.
Vital signs are monitored to rule out infection
Diet plan
Recreational and diversional activities
Family support and home care
Continuous monitoring of fluid retention or excretion
Therapeutic Management
Corticosteroids – Tab.Prednisolone
Long term side effects
hirsutism
growth retardation
GI bleeding
bone demineralization
infection
hyperglycemia
- Side effects :
behavior change and increased appetite
rounding face
weight gain
Antibiotics – for infections
Diuretics – to relief from edema
Diet restrictions: Low sodium and fluid restrictions
Diagnostic evaluation
Hematuria
Total serum protein –Low
Plasma lipids - elevated
Serum sodium- low
History
Clinical manifestation
Blood pressure normal or slightly decreased
Susceptibility to infection
Lethargic
Easily fatigued
Irritability
Ankle or leg swelling
Edema of intestinal mucosal
Labial or scrotal swelling
Pleural effusion
Urine alterations:
Decreased volume -frothy
facial edema
Weight gain
Pathophysiology
hypoalbuminemia
edema
ascites
hyperalbuminuria
The disorder can occur as
A congenital form inherited as
an autosomal recessive disorder.
A secondary disorder that occurs as
presumed cause.
in association with glomerular damage that has a known
a clinical manifestation after
A primary disease known as ,
childhood nephrosis or minimal –change nephrotic syndrome
idiopathic nephrosis
It is a clinical state that includes
Massive proteinuria
Hypoalbuminemia
Hyperlipidemia
Edema