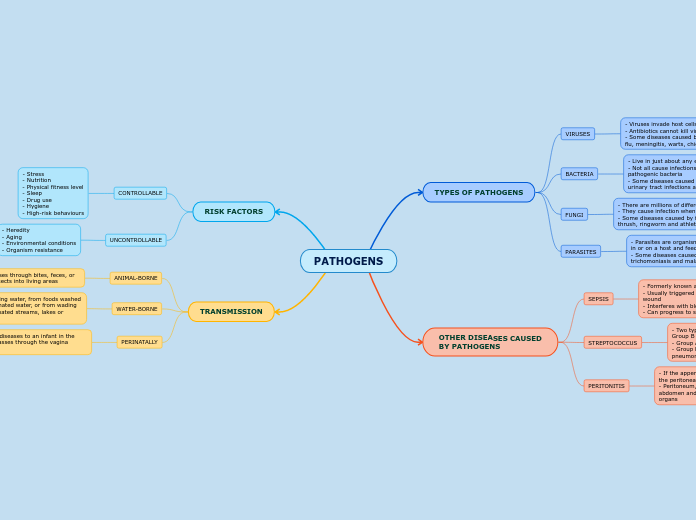
PATHOGENS
A microorganism is an organism so small that people cannot see them with the naked eye.
Microorganisms can be harmful and useful organisms.
TRANSMISSION
Harmful microorganisms include fungi, bacteria, protozoa, etc.
They cause several diseases in human beings, animals, and plants, which can even lead to death.
The harmful microorganisms not only can damage the human body, but also the food we eat.
PERINATALLY
What diseases can they cause?
- Mothers can transmit diseases to an infant in the womb or as the baby passes through the vagina during birth
WATER-BORNE
Give examples of how the spread of harmful organisms can be prevented.
- Transmitted from drinking water, from foods washed or sprayed with contaminated water, or from wading or swimming in contaminated streams, lakes or reservoirs
ANIMAL-BORNE
Give examples of how harmful organisms can spread.
- Animals spread diseases through bites, feces, or by carrying infected insects into living areas
RISK FACTORS
Research about the main characteristics of the microorganisms and give examples!
UNCONTROLLABLE
- Heredity
- Aging
- Environmental conditions
- Organism resistance
CONTROLLABLE
- Stress
- Nutrition
- Physical fitness level
- Sleep
- Drug use
- Hygiene
- High-risk behaviours
OTHER DISEASES CAUSED
BY PATHOGENS
Microorganisms help in the production of many food items, making medicines, keeping the environment clean, in manufacturing, and in research.
PERITONITIS
Microorganisms have a role in waste disposal, agriculture, and nutrient recycling.
Give examples of these types.
- If the appendix ruptures, the infectious material will spill into the peritoneal cavity and cause peritonitis
- Peritoneum, the tissue that lines the inner wall of the abdomen and covers and supports most of your abdominal organs
STREPTOCOCCUS
Give examples of bacteria used in the pharmaceutical industry.
- Two types cause infection in most people; Group A Strep and Group B Strep
- Group A Strep: strep throat, scarlet fever, etc.
- Group B Strep: In infants, can cause blood infections, pneumonia, meningitis
SEPSIS
Give examples of Microorganisms in food production.
- Formerly known as blood poisoning
- Usually triggered by a local infection such as pneumonia or a wound
- Interferes with blood flow
- Can progress to septic shock, and eventually death
TYPES OF PATHOGENS
There are five types of microorganisms. Out of these five, four can be free-living or parasitic.
There is one that can be only parasitic since it always reproduces inside other living things.
After enumerating them, click on the flags below to mark the ones which can be free-living and the ones that cannot.
can be free-living
only parasitic
PARASITES
- Parasites are organisms that behave like tiny animals, living in or on a host and feeding from or at the expense of the host
- Some diseases caused by parasites includes giardiasis, trichomoniasis and malaria
FUNGI
- There are millions of different fungal species on Earth
- They cause infection when they overgrow
- Some diseases caused by fungi includes yeast infections, thrush, ringworm and athlete's foot
BACTERIA
- Live in just about any environment, i.e. human, body
- Not all cause infections, but those that do are called pathogenic bacteria
- Some diseases caused by bacteria includes strep throat, urinary tract infections and bacterial meningitis
VIRUSES
- Viruses invade host cells within your body when infected
- Antibiotics cannot kill viruses
- Some diseases caused by viruses include the common cold, flu, meningitis, warts, chicken pox/shingles and measles