door Jeville Harry 4 jaren geleden
244
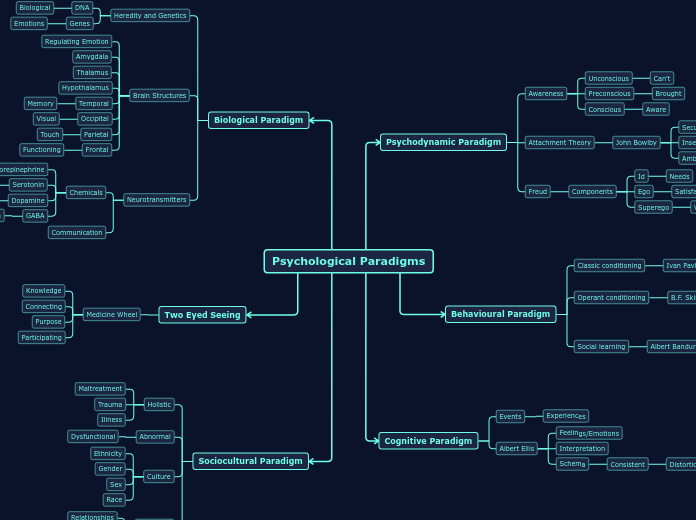
Psychological Paradigms
The text outlines various psychological paradigms, each offering unique perspectives on human behavior and mental processes. The biological paradigm emphasizes the role of genetics, brain structures, and neurotransmitters in influencing emotions and behavior.