door Theresa Ton 1 jaar geleden
132
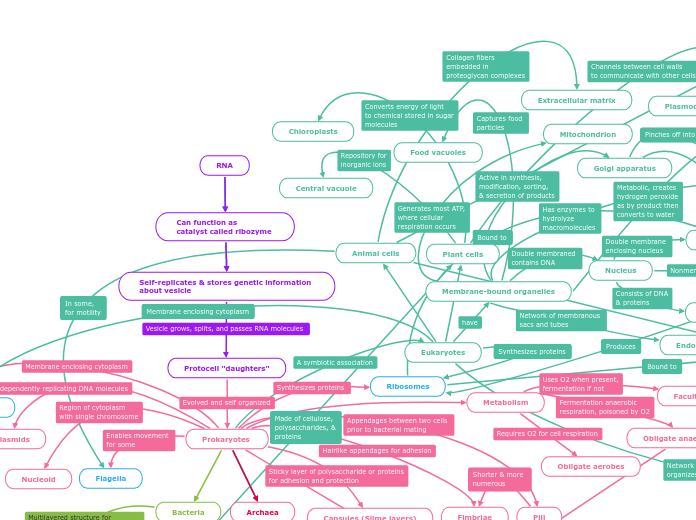
RNA
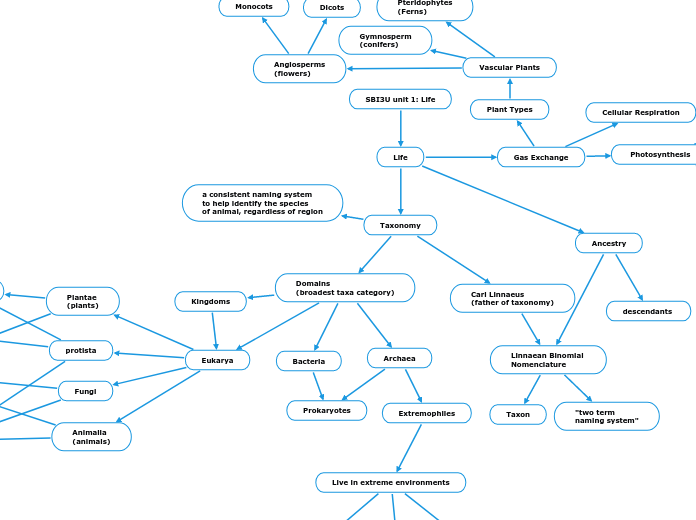
The text delves into the characteristics and classifications of cellular life, highlighting both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. It begins with RNA's role in biological processes, such as acting as a ribozyme, self-replicating, and storing genetic information within vesicles.