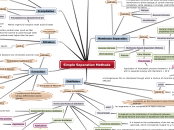
Simple Separation Methods
Distillation
Distillation as the Precursor to Gas Chromatographic Methods
non- volatile components
HPLC
volatile components
separated on a packed or capillary column
Phases in Distillation
Forms and Modes of distillation
Azeotropic/Extractive distillation
Example
Formation of two immiscible liquid phases by addition of benzene to water and ethanol.
To separate mixtures whose components boil too close together for economic fractional distillation.
Adding another component to alter the relative volatility of the mixture substances and form lower-boiling azeotrope that is heterogeneous.
Any technique used to break an azeotrope (mixtures that are difficult to separate) in distillation.
steam distillation
The mixture boiling point tempreture is reduced by vaporixing it into a stream of carrier vapor
vacuum distillation
Applications
To separate
materials that decompose below their normal boiling points.
high-boiling mixtures.
It is distillation under decreased pressure to reduces the boiling temperatures.
Flash distillation
It is instantaneous and continuous vaporization of a definite fraction of the liquid mixture in such a way that the total vapor produced is in equilibrium with the residual liquid.
Fractional distillation
It is based on the condensation of the hot vapor at verious levels in the column and the resulting liquid refluxes to a lower level where it is vaporized, which corresponds roughly to a re- distillation.
It depends on the distribution of constituents between
the liquid mixture and vapor in equilibrium with the mixture.
less volatile ones are in greater concentration in the liquid.
more volatile components concentrated in the vapor
used
for separation of the components of liquid mixtures.
related to
solids
sublimation (highly specialized distillation method), is used to volatilize their component if possible .
evaporation but all the components of interest are volatile. while volatile components are separated from non-volatile ones in evaporation.
Extraxtion
Countercurrent Extraction Versus Differential Column System
Multiple Extractions
Craig Apparatus
method of multiple liquid-liquid extractions is countercurrent extraction, which permits the separation of substances with different distribution coefficients (ratios)
Extraction of Mixtures
Successive Extractions
If Kc < 1000 -> divide some of the extraction solvent into smaller portions and for each portion use successive extractions.
If Kc >1000 -> 1 signal extraction stage is enough to extract all of the target species.
Distribution ratio D
Excluding all complications according the interactions between the extracted species and the used solvents; these interactions should be ignored to simplify the calculations. D = total concentration of solvent in organic phase/total concentration of solvent in aqueous phase
Distribution Coefficient of a Species
Distribution Coefficient is used for one species.
Distribution Coefficient Kc
Distribution of a solute concentration (C) between two solvents ( 1 and 2) during extraction can be represented by the following equation: Kc = C1/C2
Distribution of solute between two immiscible solvents
Filtration
Types of filtration
Simple filtration
Using gravitational force to separate solids from the liquid.
Using simple filter papers (made from cellulose) and exhibit particle retention levels down to 2.5 μm.
Filtration under vacuum
Using Membrane Filters
Using Buchner funnel
used to
separate solids from liquids.
Porous material with a certain particle sizes (such as filter paper or membranes) allow the solvent to pass through while retaining the solids with particle sizes higher than the pore sizes.
Precipitation
Precipitation by Adjustment of pH
Mainly organic & inorganic weak acids & bases
Precipitation via Chemical Reaction
Common ion effect
Addition of a species that form a lower solubility salt with the target species.
Solvent Precipitation
Addition of another miscible solvent to the solution which lower the solubility of the component of interest
formation of pure crystals
By carried out in (a proper solvent & a controlled manner)
formation of precipitate (PPT)
By Increase the concentration of a solute in a solution to a higher level than its solubility
Evaporation
t is the process of removing the solvent from a sample by heating or by utilizing air currents which lead to concentrate the sample or transfer it into a solid state.
example
evaporation of seawater to get sea salt salt (NaCl)
Application of heat
Using an open container for a period of time
Usage
As final step for obtaining an isolated material as a residue
As a first preparation step for further separation.
Membrane Separation
Methods
Membrane-Based Separation Methods
Electrodialysis
Ultra filtration
The process
Application of hydrostatic pressure between 1 & 10 atm to separate solutes with diameters > 20 Aْ
Structure and properties
Various semipermeable membranes
Charged Membranes
The separation is accomplished by:
exclusion of coions (ions of the same charge as
The fixed ions) from the membrane
pore size as well as
Thin Membranes
The thinner the membrane; the faster the transport rates through membranes.
Homogeneous Membranes
Particles of exactly the same size can be separated with homogeneous diffusive-type membranes when their solubilities in the film or their concentrations differ significantly
Composition
a homogeneous film or interphase through which a mixture of chemical species can be carried by molecular diffusion
Microporous Membranes
The principle
intermediate pore size -> partially rejected
<< pore size -> allowed to pass
If the size of particles (or molecules):
>>pores sizes -> rejected to pass
Separate particles that differ significantly in size.
General important properties of membranes
Good chemical stability.
Good mechanical stability
Examples
Reverse Osmosis
Dialysis
Ultrafiltration
Some Applications
Separate azeotropic mixtures
Removal of urea from blood
Convert salt water to drinkable water
Definition
It a separation process that utilize semipermeable membranes to allow passage of certain chemical species completely, while stopping or strongly restrict the permeation of others.
Crystallization
Optimal solvent composition
s designed to minimize contamination of the crystals with other materials.
oncentrating a solution containing the component of interest by
allowing it to stand
heating it
Used to
obtain pure material in the crystalline state.