Topic flotante
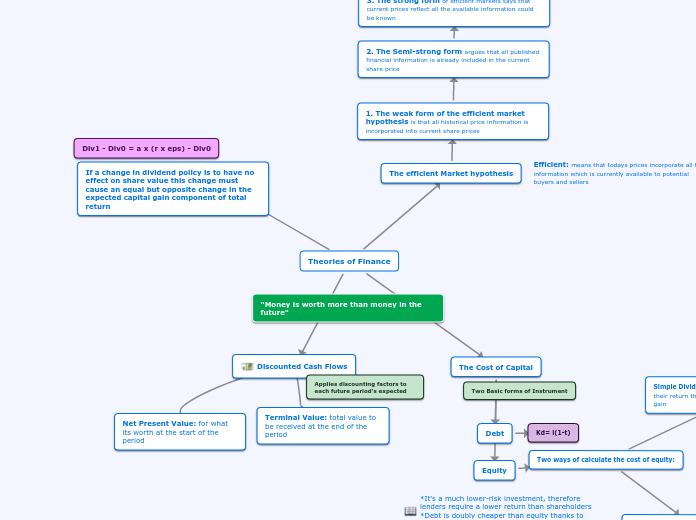
Div1 - Div0 = a x (r x eps) - Div0
If a change in dividend policy is to have no effect on share value this change must cause an equal but opposite change in the expected capital gain component of total return
Efficient: means that todays prices incorporate all the information which is currently available to potential buyers and sellers
The measure to determine how sensitive individual shares are to the return of the total stock market (BETA)
Ke= Rf + Beta (Rm-Rf)
Market Risk relates to the market as a whole. The economic cycle which would impact all companies. Market risk cannot be diversified
P= D1 / (Ke - g)
Unique risk relates to the particular company. It would include the risk of product failures, product market changes, etc
"Profits reinvested by the company will lead to larger profits and greater dividends in the future"
*It's a much lower-risk investment, therefore lenders require a lower return than shareholders
*Debt is doubly cheaper than equity thanks to tax subsidy
Two Basic forms of Instrument
Applies discounting factors to each future period's expected
Net Present Value: for what its worth at the start of the period
Terminal Value: total value to be received at the end of the period
"Money is worth more than money in the future"
Theories of Finance
Dividend Theory
The efficient Market hypothesis
1. The weak form of the efficient market hypothesis is that all historical price information is incorporated into current share prices
2. The Semi-strong form argues that all published financial information is already included in the current share price
3. The strong form of efficient markets says that current prices reflect all the available information could be known
The Cost of Capital
Debt
Kd= i(1-t)
Equity
Two ways of calculate the cost of equity:
Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM):
Risk in a financial instrument is defined as the volatility in the expected return - This high volatility in expected translates into a high required return
Simple Dividend Growth Model: Shareholders achieve their return through a mixture of dividends and capital gain
Discounted Cash Flows