VIAS DE ADMINISTRACIÓN
To name your story, you have to think about the overall message and what you want your audience to understand from the story. Also, make it relevant and easy to remember.
VÍA ÓTICA
Aplicación sobre el conducto auditivo por medio de gotas.
VÍA PARENTERAL
The ending of a story is essential. We all know that if the ending is weak, what happened before loses its importance. So make it unpredictable, but fair. A resolved ending answers all the questions and ties up any loose threads from the plot.
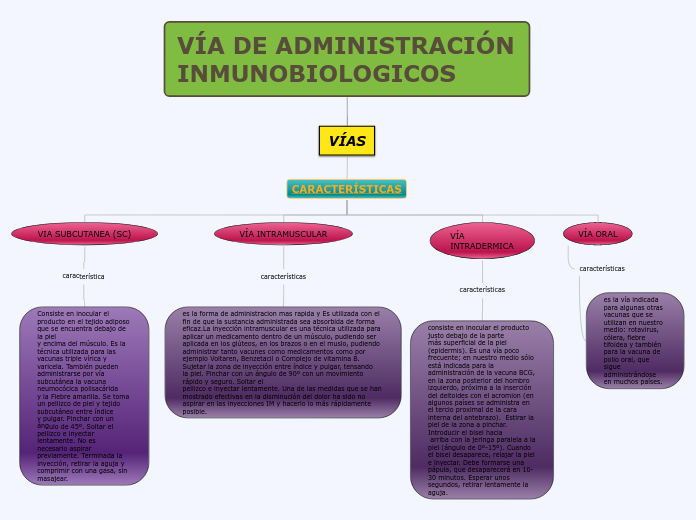
Vía intradérmica
Inyección entre las capas de la piel.
Vía subcutánea
Inyección bajo la piel.
Vía intramuscular
This is the closure section of the story.
See examples of possible outcomes below:
- all problems have been solved
- it's clear how each one of your characters ends up
- your main character is transformed by the challenge
Inyección en el musculo.
Try answering these questions to come up with a closure:
- Have all the problems been solved?
- Is there a clear picture of what happens with each character in the story?
- Has the challenge transformed your main character?
- How do the characters feel in the end?
Vía intravenosa
This is the moment when the main character surpasses the last obstacle and finally faces their greatest challenge.
The climax usually follows one of these patterns:
- realization
- resolution
- choice
Type in your answer.
Inyección en la vena.
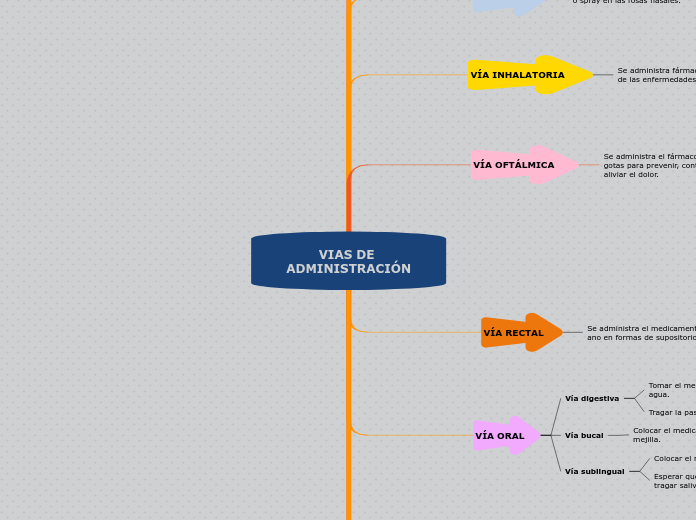
VÍA ORAL
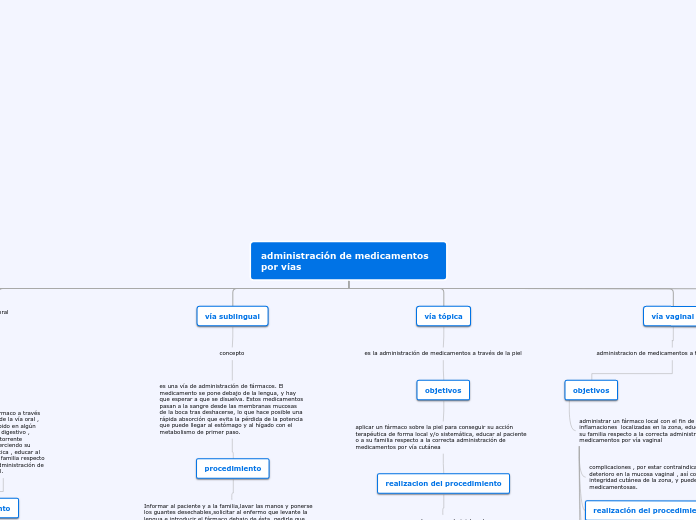
Vía sublingual
Esperar que el medicamento se disuelva, sin tragar saliva ni beber agua.
Colocar el medicamento bajo la lengua.
Vía bucal
Colocar el medicamento entre las encías o la mejilla.
Vía digestiva
Tragar la pasta sin masticar.
Tomar el medicamento acompañado con agua.
VÍA RECTAL
Se administra el medicamento a través del ano en formas de supositorios o enemas.
VÍA OFTÁLMICA
The middle of the story is where you add layers of complications that will lead to the end. Reveal more about the character's journey. Did their personality go through changes? How did they overcome the challenges? And as you build up the story’s central conflict, make it more personal to that character. Also, from the middle act, you have to lead into the final act.
Se administra el fármaco más que todo en gotas para prevenir, controlar la infección, aliviar el dolor.
Each story has a main character and that character usually needs to solve a problem or challenge. The character's challenge is the one that creates tension throughout the story.
VÍA INHALATORIA
Se administra fármacos para el tratamiento de las enfermedades pulmonares.
VÍA NASAL
Se aplica el medicamento en forma de gotas o spray en las fosas nasales.
VÍA VAGINAL
Se administra el medicamento por la vagina a través de pomada, comprimidos y óvulos vaginales.
VÍA TÓPICA
In the beginning of the story (or the exposition), you will need to introduce the setting and characters. You might also want to introduce the main conflict. This part of the story is important because it gives the reader necessary background information and maybe even a first insight into a character’s personality.
Vía cutánea
Se aplica en forma de geles, pomada, lociones.