door Estefania Romero Garcia 1 jaar geleden
118
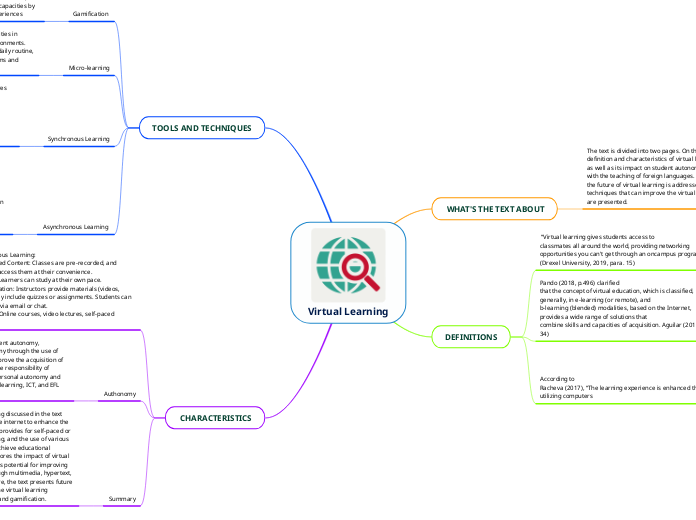
Virtual Learning
Virtual learning encompasses a range of educational practices facilitated by the internet, including e-learning and blended learning modalities. It significantly influences student autonomy, encouraging self-directed learning through various tools and flexible access to pre-recorded content.