av Ethan Attwood 11 år siden
904
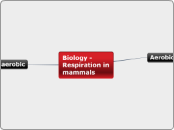
Biology - Respiration
In mammals, respiration can occur aerobically or anaerobically. Aerobic respiration, which requires oxygen, involves the breakdown of glucose to produce carbon dioxide, water, and a significant amount of energy.