Muscular System
It is constituted constituted by the muscular cells and sheaths with the connective tissue that cover them and connect the muscular masses with the rest of the locomotor system
Tendons are connected from the muscles to the bones, and the ligaments are conected between to bones (in the joints)
Muscle Cells
Smooth
Its located in the wall of the hollow viscera, such as intestine, stomach, and blood vessels.
Cardiac
It is located around the heart.
The sarcomere is the functional unit of the striated muscle (carddiac and Skeletal)
Components of the sarcomere:
a) Thin filaments of actin and other proteins
b) Thick filaments of myosin
c) Z disks or lines
Skeletal
This muscles are conected to the bones and participate in locomotion and maintaining posture
Circulatory System
Is made up of blood, heart and blood vessels. Its function is to bring oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells and eliminates waste products.
Blood
It has a liquid consistency, and the average volume of blood in human body goes from 5 to 6 liters. It is made of 55% plasma and the rest is formed by cells.
The heart pumps blood to the whole body. It is a hollow muscular organ divided into four cavities; two atriums and two ventricles.
It is composed by four segments:
-Left atrium
-Left Ventricle
In this passes the oxigenated blood from the lungs and gets into the aorta arteny
-Right atrium
-Right Ventricle
In this passes blood from the veins and passes into the lungs to get oxigenated.
It is a hollow muscular organ located in the middle of the lungs, inside the torax
Skeletal System
It takes care ofbody locomotion and provides the basic morphology of the body that is to stand in two feet
Cells
-Osteochondrogenic and osteogenic: are capable of developing into osteoblast and finally osteocyte.
-Osteoblasts: actively synthesize the bone matrix
-Osteocyte: is the mature cell
-Osteoclast: The cell that reabsorbs bone. That is, degrades bone matrix
Functions
-Support of the whole organism
-Participates in locomotions
-Protects vital organs
-It is the main reservoir of ions, calcium, and phosphate
-Contains the red bone marrow
Divides in two sections
Appendicular Skeleton:
- The extremities
Axilar Skeleton:
- Head
- Torso
Types of bones
Spongy: Consists of trabecular. The characteristic of this type of bone is that there are large spaces in which other tissues are lodged. Spongy bone is not as strong as the compact.
Compact: Osteone is the basic structural unit of bone tissue; it is constituted by the Havers canal, through this tunnel the vascular elements that supply the bone pass; and around it are the lamellae containing bone cells.
Lymphatic System
Is a network of organs, lymph nodes, ducts and lymphatic vessels
Lymph
Consisting of water, electrolytes and proteins, that come from the blood, circulate through the lymphatic vessels and turn into the veins, is the intermediate in the nutritional change between blood and tissues.
Function
Produces and transports lymph from the tissue to the bloodstream, returning the antibodies formed in the lymph nodes to the blood transporting cholesterol into the circulation through the blood vessels
The vessels lead a clear fluid (lymph) to the large venous vessels of the neck through the right lymphatic duct.
The thoracic duct begins in the abdomen, rises through the thorax and neck and empties it in the left jugular veins of the internal and subclavian veins.
Immune System
The immune system has the function to recognize the components of our body and discriminate them from those that are not.
Tissue and Organs
Thymus: it is an encapsulated primary lymphoid organ, that is able to distinguish between "What is proper" and "what is not"
-Positive selection: T lymphocytes that are able to recognize both molecules of the body, as those that aren't.
-Adverse selection: lymphocytes are removed
Lymphoid organs: bone marrow, thymus, lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils, and mucosa in lymphoid tissue (MALTS).
Tonsils: protects the organism from antigens that enter by air or that are ingested
Spleen: filters blood, eliminates or inactivates antigens, destroys old platelets and erythrocytes.
Lymph nodes: its function is to filter blood, eliminate or inactivate antigens, destroy old platelets and erythrocytes.
Responses
Adaptive immunity
Has a more delayed response, because it takes more time to take action. It has memory, that vertebrates have cells capable of recognizing, and it is specific for each pattern of pathogens.
When an outer substance activates the immune system,the lymphocytes recognize molecules of viruses and bacteria on the surface.
Innate immunity
Is the first line of defense, it has an immediate response. It acts when it's in contact with pathogenic microorganisms.
Components: a) physical barriers, such as skin and mucous; b) cellular components, macrophages, neutrophils, eosinophils, etc.; and c) proteins, such as complements in plasma.
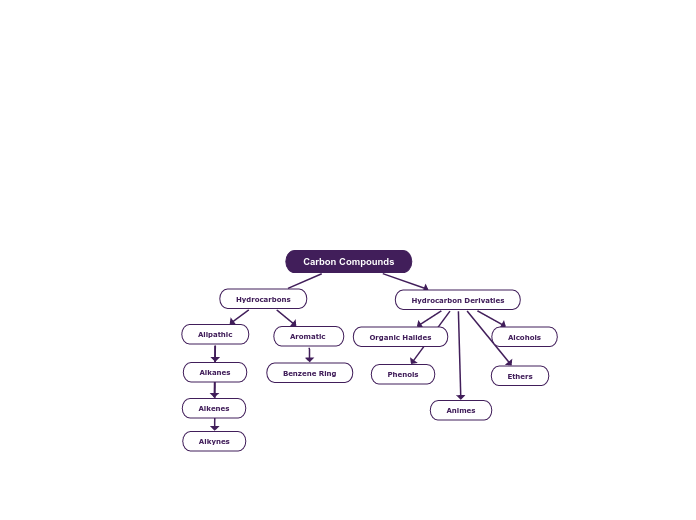
Carbon Compounds
Hydrocarbon Derivaties
Animes
Ethers
Phenols
Alcohols
Organic Halides
Hydrocarbons
Aromatic
Benzene Ring
Alipathic
Alkynes
Alkenes
Alkanes