av Korawich Keereerak 5 år siden
343
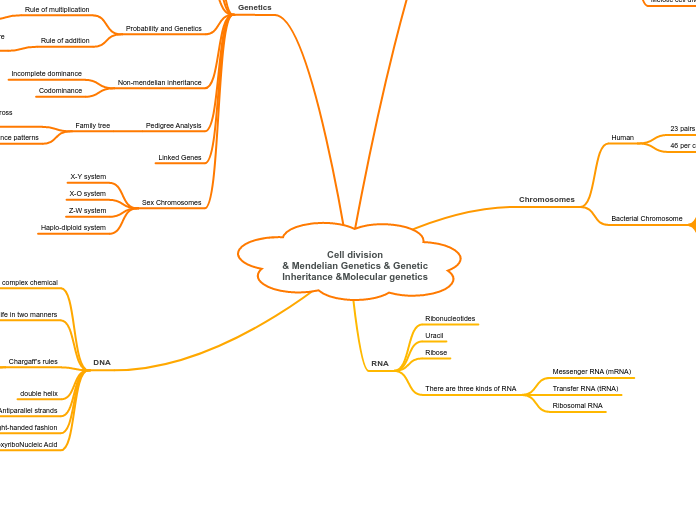
Cell division & Mendelian Genetics & Genetic Inheritance &Molecular genetics
av Korawich Keereerak 5 år siden
343

Mer som dette
Inheritance patterns
interrelationships of parents and children across generations
Chance that an event can occur 2 or more different ways
– probability of Bb x Bb -> Bb
– sum of the separate probabilities
Chance that 2 or more independent events will occur together
– probability of Pp x Pp -> pp
Members of one gene pair segregate independently from other gene pairs during gamete formation
genes become separated in gamete formation
The ratio of two classes of progeny was 3 : 1
In F 2, the missing trait reappears in ¼ of the progeny
F 1 progeny resembles one of the parents
Stage of Meiosis
telophase II,
the chromosomes arrive at opposite poles
Subtopic
anaphase II
the sister chromatids separate.
metaphase II
the sister chromatids are arranged at the metaphase plate
Meiosis II
is very similar to mitosis
telophase I
anaphase I
One chromosome of each pair moves toward opposite poles, guided by the spindle apparatus.
metaphase I
pairs of homologs line up at the metaphase plate, with one chromosome facing each pole.
prophase I
chromosome pairs with its homolog (synapsis) and crossing over occurs
Objectives
To produce reproductive cells
. Sexual life cycle
Cells that can undergo mitotic cell division include
Shoot and root apical meristems of plant tissue
Epithelial cells, Bone marrow of animal tissues
Mitosis and cytokinesis
Cytokinesis occurs during telophase
In plant cells, a cell plate forms during cytokinesis
In animal cells, cytokinesis occurs by a process known as cleavage, forming a cleavage furrow
Mitosis
Telophase
Anaphase
Metaphase
Prometaphase
Prophase
Interphase
Chromosomes are duplicated only during the S phase.
The cell grows during all three phases
- Can be divided into 3 phases
G2 phase
S phase
G1 phase
~90% of the cell cycle
consist of chromatin
Linear chromosome
Not associated with proteins
Circular chromosome