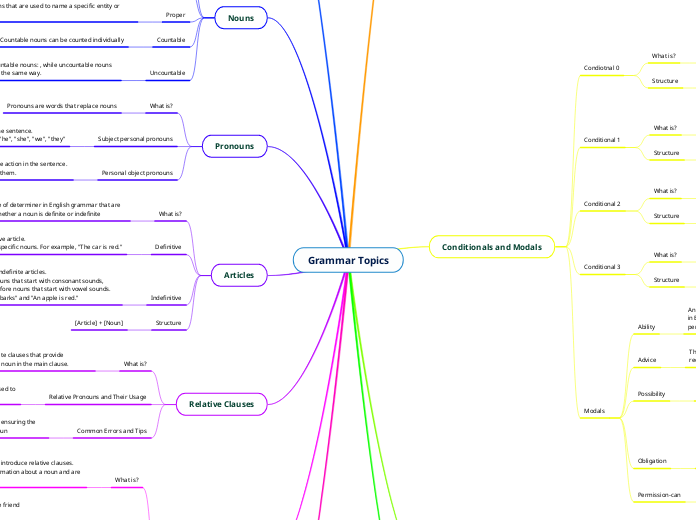
Grammar Topics
Adverbs
Types
Adverbs of manner: These adverbs describe how an action is done. For example, in the sentence "She sings beautifully," the adverb "beautifully" describes how she sings.
Adverbs are a type of word that modifies verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
Relative Pronouns
Function in Sentences
Relative pronouns are used to join two sentences or phrases where one describes or identifies the noun in the other.
Types of Relative Pronouns
Whose" indicates possession and can refer to people or things. For example, "The man whose wallet was lost has found it."
That" can refer to people, animals, or things. For instance, "The car that I bought is red."
Which" refers to animals and things. For example, "The book which is on the table is mine."
Who" and "whom" refer to people. For instance, "The friend whom I invited is coming."
Relative pronouns are words that introduce relative clauses. These clauses provide more information about a noun and are connected to the main sentence
Relative Clauses
Common Errors and Tips
Watch out for misplaced or dangling modifiers, ensuring the relative clause clearly refers to the intended noun
Relative Pronouns and Their Usage
Relative pronouns (who, whom, whose, which, that) are used to connect relative clauses to the nouns they modify.
Relative clauses are subordinate clauses that provide additional information about a noun in the main clause.
Articles
[Article] + [Noun]
Indefinitive
A" and "an" are the indefinite articles.
"A" is used before nouns that start with consonant sounds, while "an" is used before nouns that start with vowel sounds. For example, "A dog barks" and "An apple is red."
Definitive
The is the definitive article.
It is used before specific nouns. For example, "The car is red."
Articles are a type of determiner in English grammar that are used to specify whether a noun is definite or indefinite
Pronouns
Personal object pronouns
These are used as the object of the action in the sentence.
Examples:me, you, him, her, it, us, them.
Subject personal pronouns
These act as the subject of the sentence.
Examples include "I", "you", "he", "she", "we", "they"
Pronouns are words that replace nouns
Nouns
Uncountable
Countable and uncountable nouns: , while uncountable nouns cannot be counted in the same way.
Countable
Countable nouns can be counted individually
Proper
These are nouns that are used to name a specific entity or person.
Common
They are nouns that are used to refer to people, places or things in general
Nouns are words used to name people, places, things or ideas
Determiners
Article
Articles are a type of determiner.
Numbers
Numerals like "one," "two," "three,
Interrogative
These are used in questions to ask about specific items. For example, "which" and "whose."
Possessive
These show ownership. They are similar to possessive pronouns and include words like "my," "your," "his," "her," "its," "our," and "their."
Quantifiers
These indicate the quantity of a noun. Examples include "some," "many," "few," and "several."
Demostrative
These indicate specific items in space or time. For example, "this," "that," "these," and "those."
Determiners are words or a group of words that precede a noun and help specify what the noun refers to
Infinitives
Examples
Eat
Sit
To eat
To sit
Zero infinitive
The zero infinitive = base
To infinitive
The to-infinitive = to + base
An infinitive is a verbal consisting of the word to plus a verb and functioning as a noun, adjective, or adverb
Passive Voice
Passive Voice Structure
Object+verb+subject
Active Voice Structure
Subject+verb+object
Is a gramtical structure used when we don't want to emphasize who or what performs the action, but rather emphasize who or what receives it
Conditionals and Modals
Modals
Permission-can
This modal is used to express the ability to ask for a confirmation to do something or capacity to do something
Obligation
Obligation has to types of modals:
must
have to
should
the porpose of it is to gave a person or obligate a person to do something
Possibility
Is used to express events or situations that are possible to happen but its not sure that it can occur.
Advice
The modal verb of advice is "should." It indicates a recommendation or suggestion
Ability
An ability modal, such as "can," "could," or "be able to," is used in English to indicate a person's capacity or capability to perform a specific action or task
Conditional 3
If+past perfect,perfect conditional
The type 3 conditional refers to an impossible condition in the past and its probable result in the past
Conditional 2
past simple+would+verb
The second conditional is the one we use when we talk about things, usually unreal, that are very unlikely to happen.
Conditional 1
If+present simple+will/wont+infinitive
The first conditional is a type of if-else statement in English that allows you to express a possible scenario or condition and its possible consequences.
Condiotnal 0
If+present simple,...Present simple
A type of conditional sentence that expresses a general truth or fact, where the result is always true when the condition is met
Past tenses and future with will and going to
Future going to & Will
Going to: SUBJECT+ AM/IS/ARE+ going to+ infinitive
Will: SUBJECT+ Will+ infinitive + complement
Will is used when referring to the future with certainty and for recent, rapid decisions. Going to is used to refer to events that have been previously planned.
Past Perfect
Had+S+past partciple+object?
S+had not+past partciple+object
S+had+past participle+object
The past perfect is used in the same way as the present perfect, but it refers to a time in the past, not the present.
Past Continuous
Structure
Was/Were+subject+verb in ing+object?
Subject+was/were+not+verb in ing+object
Subject+was/were+verb in ing+object
What is?
The past continuous tense, also known as the past progressive tense, describes ongoing actions in the past
Past Simple
What Is?
The simple past tense, according to the Cambridge Dictionary, is defined as “the form of a verb used to describe an action that happened before the present time and is no longer happening
Did+subject+infinitive without to?
Subject+did not+infinitive without to
Subject+verb+ed