av Yuly Pilco 2 år siden
379
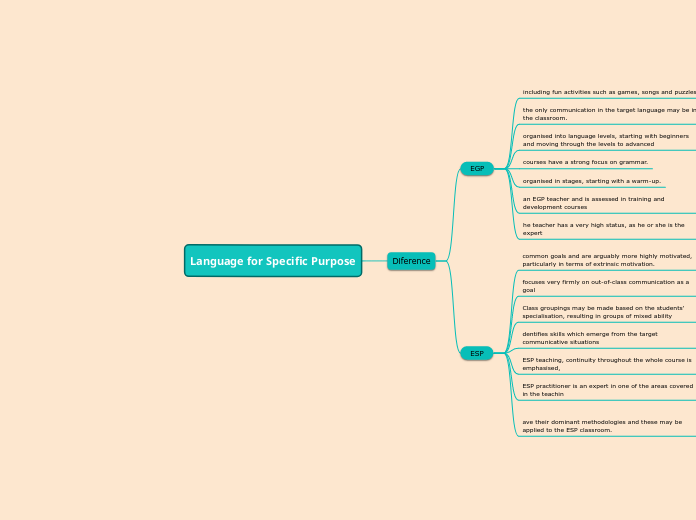
Language for Specific Purpose
av Yuly Pilco 2 år siden
379

Mer som dette
Example
medical students may be familiar with problem-based learning and business students may be familiar with a case-study approach