av Taylor Johnson 5 år siden
396
Tree organigram
av Taylor Johnson 5 år siden
396

Mer som dette
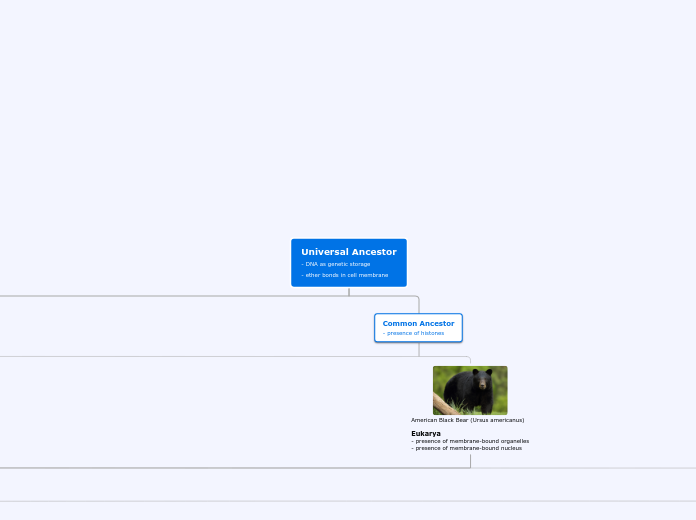
Opisthokonta - single posterior flagellum on swimming cells
Animals - multicellularity - absorptive heterotroph - mobility - complex organ systems - gametic life cycle
Giant Barrel Sponge (Xestospongia muta) Porifera
Eumetazoa
Moon Jelly (Aurelia aurita) Cnidaria - diploblasty - radial symmetry
Medusozoa
Pennaria disticha Hydrozoa - polyp and medusa
Moon Jelly (Aurelia aurita) Scyphozoa - usually only medusa
Elkhorn coral (Acropora palmata) Anthozoa - usually only polyp
Bilateria
Deuterostomia - radial and indeterminate cleavage
Chordata - notochord - dosal nerve cord - pharyngeal slits - endostyle
Branchiostoma lanceolatum Cephalochordata - notochord - hollow dorsal nerve cord - pharyngeal slits - post-anal tail
Sea Peaches (Halocynthia aurantium) Urochordata - notochord - hollow dorsal nerve cord - pharyngeal slits - post-anal tail
Vertebrates
Agathans - notochord - hollow dorsal nerve cord - pharyngeal slits - post-anal tail - cranium - vertebral column - cartilaginous skeleton - ectothermic
Chondrichthyes - notochord - hollow dorsal nerve cord - pharyngeal slits - post-anal tail - cranium - vertebral column - jaws - cartilaginous skeleton - ectothermic
Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) - notochord - hollow dorsal nerve cord - pharyngeal slits - post-anal tail - cranium - vertebral column - jaws - bony skeleton - lungs or lung derivatives - ectothermic
Lobe-finned fishes - notochord - hollow dorsal nerve cord - pharyngeal slits - post-anal tail - cranium - vertebral column - jaws - bony skeleton - lungs or lung derivatives - ectothermic
Amphibia - notochord - hollow dorsal nerve cord - pharyngeal slits - post-anal tail - cranium - vertebral column - jaws - bony skeleton - lungs or lung derivatives - limbs - ectothermic
Reptilia - notochord - hollow dorsal nerve cord - pharyngeal slits - post-anal tail - cranium - vertebral column - jaws - bony skeleton - lungs or lung derivatives - limbs - ectothermic (non-bird reptiles) - endothermic (birds) - amniotic egg
Mammalia - notochord - hollow dorsal nerve cord - pharyngeal slits - post-anal tail - cranium - vertebral column - jaws - bony skeleton - lungs or lung derivatives - limbs - endothermic - amniotic egg - hair - milk
Giant Sea Star (Pisater giganteus) Enchinodermata - spiny skin - water vascular system - adults radially symmetrical, larvae are bilaterally symmetrical - no brain - complete digestive tract
California sea cucumber (Apostichopus californicus) Holothuroidea
Asteroidea
Serpent Star (Ophiura ophiura) Ophiuroidea
Purple Sea Urchin (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus) Enchinoidea
Protostomia - spiral and determinate cleavage - blastopore becomes mouth
Lophotrochozoa - trochophore and/or lophophore larvae
Pork Tapeworm (Taenia solium) Platyhelmnithese - acoelomates - incomplete digestive tract - no respiratory or circulatory systems
Pork Tapeworm (Taenia solium) Cestoda (Tapeworms) - parasitic - no digestive tract
Macrostomum lignano Rhabditophorans (Free-living)
Sheep Liver Fluke (Fasciola hepatica) Trematoda - parasitic
Common ancestor
Mollusca - soft-bodied - foot, visceral mass, mantle - coelomates - organ systems
Soft Shell Clam (Mya arenaria) Bivalvia - two-part shell
Humboldt squid (Dosidicus gigas) Cephalopoda - reduced or absent shell (except nautilus) - closed circulatory system
Golden Apple Snail (Pomacea canaliculata) Gastropoda
Common Earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris) Annelida - segmented worms - closed circulatory system - complete digestive tract
Ecdysozoa - metamorphosis (most) - ecdysis
Anthropoda - "jointed foot" - segmented - exoskeleton made of chitin - complete digestive tract - open circulatory system
Pancrustaceans
Monarch butterfly (Danaus plexippus) Hexapoda - six legs - insects - many have wings (crucial to their success as a group) - head, thorax, abdomen
Chesapeake Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus) Crustaceans - cephalothorax
Southern Black Widow (Latrodectus mactans) Chelicerates - cephalothorax and abdomen - 4 pairs of walking legs, pedipalps, and chelicerae
Roundworm (Caenorhabditis elegans) Nematodoa - free-living and parasitic - cuticle - pseudocoelom - complete digestive tract
Fungi - multicellularity - absorptive heterotroph - cell wall - zygotic life cycle
slime molds Amebozoa - movement with pseudopodia
Rhizaria - filose pseudopodia
radiolarians
foraminiferas
dinoflagellates Alveolata - membranous vesicles on cell membrane - secondary plastids
Stramenopila - tripartite flagellar hair - secondary plastids
diatoms
giant kelp
Fly Agaric
euglenoids
Plants
Angiosperms - pollen - seed - fruit - flowers - endosperm - heterospory - wood - ovules - ovaries
Gymnosperms - pollen - seed - heterospory - wood - ovules
Monilophytes - sporic life cycle - embryo - desiccation resistant spores - apical meristems - gametangia - sporangia - lignin - xylem and phloem - megaphylls - dominant sporophyte generation - thick waxy cuticle - stomata
Lycophytes - sporic life cycle - embryo - desiccation resistant spores - apical meristems - gametangia - sporangia - lignin - xylem and phloem - leaves (lycophylls) - dominant sporophyte generation - thick waxy cuticle - stomata
Hornworts - sporic life cycle - embryo - desiccation resistant spores - apical meristems - gametangia - sporangia
Mosses - sporic life cycle - embryo - desiccation resistant spores - apical meristems - gametangia - sporangia
Liverworts - sporic life cycle - embryo - desiccation resistant spores - apical meristems - gametangia - sporangia
Charophytes
Common Ancestor
chlorophytes
rhodophytes