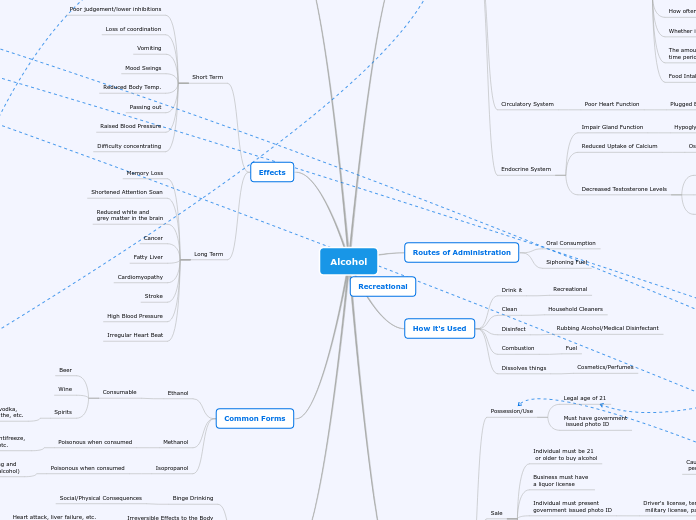
Alcohol
How it Works
Digestive System
~ 20% of alcohol absorbed in the stomach
~ 80% of alcohol absorbed in the small intestine
Liver
Free radicals damage the liver
Liver cirrhosis
Stomach
Alcohol increases acid content in the stomach
Sever stomach pain/sores
CNS
Brain
Slowed reaction time
Foggy thinking/memory
Weakened muscles
Impaired vision
Dulled hearing
Damage/Kill Neurons
Factors Effecting CNS Impairment
Age, weight and sex
Women produce less alcohol
dehydrogenase than men
Women are usually smaller
and lighter than men
Further concentrates the
alcohol in their blood
Mood/psychological
makeup of individual
Genetic Background
How often the individual drinks
Whether it's mixed with other drugs
The amount of alcohol/
time period over which it was drunk
Food Intake
Circulatory System
Poor Heart Function
Plugged Blood Vessels
Damaged cells
Endocrine System
Impair Gland Function
Hypoglycemia
Reduced Uptake of Calcium
Osteoperosis
Decreased Testosterone Levels
Erectile Dysfunction
Easy Bruising
Acne
Routes of Administration
Oral Consumption
Siphoning Fuel
How it's Used
Drink it
Recreational
Clean
Household Cleaners
Disinfect
Rubbing Alcohol/Medical Disinfectant
Combustion
Fuel
Dissolves things
Cosmetics/Perfumes
Regulation
Possession/Use
Legal age of 21
Must have government
issued photo ID
Sale
Individual must be 21
or older to buy alcohol
Business must have
a liquor license
Individual must present
government issued photo ID
Driver's license, temporary permit,
military license, passport, etc.
Business cannot offer free alcohol with meals
Restrictions on alcoholic specials (two-for-one) and happy hours
Some states prohibit sale to pregnant women
Distribution
Distribution laws/regulations
vary state to state
Oregon Liquor
Control Commission
Wine, Liquor and Malt
Beverage Privilege Tax
Too many things to list; https://www.oregon.gov/olcc/Pages/index.aspx
Also handles marijuana laws
Importation
Must have Federal Basic
Importers Permit
Must maintain and staff
a business office in U.S.
Must contract with an
existing U.S. licensed importer
Must posses Certificate of Label
Approval for each imported product
Must pay taxes, fees and duties
Obtain Certificate of Age and Origin
for certain wines and spirits
Customs paperwork
Classification
Depressant
Relaxation
Slurred Speech
Modified Equilibrium
Relieves Anxiety
Effects
Short Term
Poor judgement/lower inhibitions
Loss of coordination
Vomiting
Mood Swings
Reduced Body Temp.
Passing out
Raised Blood Pressure
Difficulty concentrating
Long Term
Memory Loss
Shortened Attention Soan
Reduced white and
grey matter in the brain
Cancer
Fatty Liver
Cardiomyopathy
Stroke
High Blood Pressure
Irregular Heart Beat
Common Forms
Ethanol
Consumable
Beer
Wine
Spirits
Gin, whisky, vodka,
tequila, absinthe, etc.
Methanol
Poisonous when consumed
Used in fuel, antifreeze,
paint thinner, etc.
Isopropanol
Poisonous when consumed
Used for disinfecting and
cleaning (rubbing alcohol)
Concerns
Binge Drinking
Social/Physical Consequences
Irreversible Effects to the Body
Heart attack, liver failure, etc.
Social Consequences
Intervention
Bankruptcy
Job Loss
Relationship Destruction
Marijuana
Common Forms
Dried flowers, stems and leaves
Edibles
Candies, brownies, cereals, drinks, etc.
THC
The chemical that gets you high
CBD
The chemical used for pain relief
Concentrates
Lotions, patches oils, etc.
Also contain THC, CBD or both.
Routes of Administrations
Smoking
Dried parts of cannabis plant
Oral Consumption
Edibles/oils
Topical
Lotions, creams, oils, etc.
Concerns
Addiction
Giving up social events to use marijuana
Failure to quit using marijuana
Affects job, relationship or school
Brain
Short Term
Attention, memory and mood
Long Term
Affects brain development and
establishing neural connections
Use during pregnancy
impairs attention, memory and
problem solving skills of children
May lead to problems
with behavior
Poisoning
Can occur with edibles
People can eat much because edibles
don't have an immediate effect
Classification
Depressant
See "Alcohol"
Stimulant
Increases CNS activity
Hallucinogenic
Causes changes in thought,
emotion or conciousness
Effects
The "high" caused by
dopamine release
May increase risk
for depression
May worsen symptoms of mental disorders already present
Colors may seem brighter
Noises may seem louder
Distortion of time
Lower inhibitions
Decrease coordination/reaction time
How It's Used
Personal Use
Medical Use
Must have severe medical condition
and diagnosed by doctor or osteopath
May have 6 mature plants
May have 18 immature
plants, starts or seedlings
Commercial
Wholesale
Retail
Processing
Production
Industrial Hemp
Cannabis sativa
with less than 0.3% THC
Clothing, cosmetics, industrial materials, etc
Production, possession and
commerce legal in Oregon since 2010
How it Works
THC mimics brain
chemical Anandamide
THC can bind to
cannabinoid receptors
altering psychological function
Alters hippocampus
and orbitofrontal cortex
Involved in making new
memories and change attentional focus
Alters cerebellum/ganglia
Control posture, balance,
coordination and reaction time
Activates reward system
Releases dopamine
Causes high, making
people want more
Regulation
Illegal at Federal Level
Legal for Recreational
Use in Some States
Possession/Use
Must be 21 or older
Must have valid government issued photo ID
May have up to 8 ounces of
usable marijuana in their homes
May have 1 ounce on their person in public
16 ounces of solid cannabinoid
product in solid form
72 ounces of a cannabinoid
product in liquid form
5 grams of cannabinoid extracts
Cannot use in bar/reseraunt
Sale
Distributions
Growing
Individuals may grow up to 4 plants on their property
May have 10 marijuana seeds
Importation
Cannot take marijuana across state lines
Synthetic marijuana is illegal in Oregon
Tobacco
Common Forms
Cigarettes
Cigars
Little Cigars
Cigarillos
Water pipes (hookas)
Smokeless tobacco
Chewing tobacco
Loose-leaf tobacco
E-cigarettes
Pen style, box style,
rechargeable, variable voltage
Prefilled capsules, refillable
capsules, disposables
Dissolvable Products
Orbs, Sticks/Strips
Classification
Both stimulant and depressant
How it Works
Mimics acetylcholine
Stimulates and then depresses
cholinerergic receptors
Concerns
Addiction
Causes change in brain
Secondhand Smoke
Lung cancer
Premature heart disease
Respiratory infections
Lung Cancer
80% of people with lung
cancer are smokers
Economic costs
Smoking-related illness costs ~$300 billion/year
~$170 billon in direct medical care
~$156 billion in lost productivity
~$5.6 billion in lost productivity
from secondhand smoke
How It's Used
Recreation
Regulation
Import
Over 21
May not exceed US customs
limit for personal use
May bring back 200 cigarettes
AND 100 cigars at once w/o permit
Tobacco Importer Permit
Usually for businesses
May bring up to 1,000 cigarettes
every 31 days from American Samoa,
Guam, the Commonwealth of the Northern
Mariana Islands or the US Virgin Islands
No more than 200 of the 1,000
can be sourced outside of these areas.
Cuban Cigars
Can be imported personally as long
as you have them with you at the border.
Cannot be imported commercially
Permits
Tobacco Importer Permit
For anyone who wants to import foreign tobacco to US
Importer of Processed Tobacco
For businesses wanting to import
processed tobacco to US
Don't need if you already
have Tobacco Importer Permit
Tobacco Products Manufacturer
Importers may need this depending
on how they prepare their product for sale
Have to report to FDA
Export
Permits
Tobacco Export Warehouse Proprietor
For businesses looking to export American tobacco
Do not have to report to FDA
Guidelines
Must be in accordance with the
specifications of the foreign purchaser
Not in conflict with laws of country it's exported to
Labelled on outside of package that it's intended for shipping
Not sold or offered for sale in domestic commerce
Consumer Use
Must be 21
Manufacturing in US
Permits
Tobacco Products Manufacturer
For businesses that manufacture tobacco products
Manufacture of Processed Tobacco
For businesses that manufacture processed tobacco
Tobacco Control Act (2009)
Restricts tobacco marketing and sales to youth
Bans sale to minors, vending machine sales, sales with packages of less than 20 cigarettes, tobacco brand sponsorship of sports, entertainment events, social and cultural events, free giveaways of sample cigarettes.
Allows FDA regulation of tobacco
Can regulate nicotine and ingredient levels
Requires smokeless tobacco products to have warning labels
May cause mouth cancer, is addictive, is not a safe alternative to smoking, may cause gum disease and tooth loss
Packaging
Must be on two principle sides and cover at least 30% of packaging
Ads
Warning label must cover at least 20% of ad area
"Modified Risk" claims must be
supported by scientific evidence
Tobacco companies must file an application for a modified risk tobacco product and be given the order to advertise as such
Requires disclosure of tobacco ingredients on packaging
Preserves state, local and tribal authority
May regulate tobacco in certain respects
Tobacco companies and suppliers must register with FDA annually
Must open facilities for FDA inspection every 2 years
Bans cigarettes with characterizing flavors except menthol and tobacco
Effects
Increase heart rate/blood pressure
Atherosclerosis
Increases blood flow to heart
Atherosclerosis
Heart Attack
Heart disease
Decreases blood oxygen levels
Increase cholesterol deposition
Routes of Administration
Inhalation of Smoke/Vapor
Oral - stays between lip and front teeth
Oral - dissolves
Caffeine
Classification
Stimulant
Psychoactive drug
What it's used for
Recreation
Medication
Found in many over-the-counter pain relievers
Effective treatment for migraines
Routes of Administrations
Usually oral
Can be administered intravenously, but not common
Regulation
Not strictly regulated; FDA suggests no more that 400 mg/day for a healthy adult, discouraged for children
Importation
Process
Mark Country of Origin clearly on each bag
Fill out Country of Origin certificate
Importer Security Filings filed no later than 48 hours before shipments estimated time of departure from last foreign port
Must fill out Customs and Border Protection form five days before import arrives
Negotiate contract with grower looking to export to America
Must be named representative of contract
Outline payment method
Designate the territory of growing and make sure it's exclusive for your use
Open credit line to avoid hang-ups, refrain from paying in cash
Credit line should outline ports of entry in US
List documents you need for customs and have them handy
Hire customs broker to manage importation
Make transportation plans for product once it enters US
No limit on importation amount for coffee or tea
Guidelines for FDA inspection of samples
100 bags or less; 6 bag samples
101-200 bags; 10 bag samples
201-1000 bags; 15 bag samples
Over 1000; 20 bag samples
Most coffee imports are tax free
Excludes coffee containing syrups or sauces
How it Works
Blocks adenosine receptors in the brain
Allows dopamine to be active
Effects
Blocks body's ability to feel tired
Increased alertness, activity, body temperature
Restlessness, excitability and dizziness
Irritability and anxiety
Dehydration and increased need to urinate
Fast breathing and heart rate
Headache, lack of concentration, stomach pain
Long term effects
Nervousness, difficulty sleeping, anxiety, muscle tremors and weakness, fatigue, poor appetite, nausea, low blood pressure, etc.
Common Forms
Teas
Brewed black, 8oz
47 mg
Brewed black, decaf, 8oz
2 mg
Brewed green, 8oz
28 mg
Ready-to-drink, 8oz
19 mg
Sodas
Colas may not contain more that 6mg/ounce
Citrus, 8oz
0 mg
Root beer, 8oz
0 mg
Coffee
Brewed, 8 oz
96 mg
Brewed, decaf, 8oz
2 mg
Espresso, 1oz
64 mg
Espresso decaf, 1oz
0 mg
Instant, 8oz
62 mg
Instant, decaf
2 mg
Chocolate
Milk
20mg/100ml
Dark
59mg/100ml
Snack bars/energy drinks
Guarana
Energy drink, 8oz
29 mg
Energy shot, 1oz
215 mg
Concerns
Withdrawal
Headache, fatigue, low energy, depression, anxiety, tremors, poor concentration
Over consumption
May lead to heart attacks
Over 90% of adults use caffeine regularly
Tremors, nausea, vomiting, very fast/irregular heart beat, confusion, panic attacks, seizures
Tropical Economical Collapse
Many tropical areas rely solely
on coffee bean exportation
Climate change is
decreasing coffee bean yield
Coffee tree must have specific balance of sunlight,
soil pH, water and temperature to thrive
Increasing temp has allowed fungus
(hemileia vastatrix) to invade
Causes gradual yellowing and decaying of leaves, leaving berries at the mercy of animals and weather conditions
Coffee may become a luxury
Only Hawaii and California can
produce coffee beans
California
Doesn't get enough water
Hawaii
Land is expensive, so coffee prices increase
Meth
Common Forms
Powder (common)
Crystalline (common)
Pills
Meth Base (less common)
Waxy, gooey oil
Colors
Pure meth
Translucent or white
Impure meth
Blue, yellow, orange, pink, brown, etc.
Color depends on how it's made
and what it's cut with
Classification
Stimulant
Effects CNS
How It Work
Brain
Forces neurons to release stored
noradrenaline and dopamine at once
Increases dopamine in brain by ~10x
the amount of any pleasurable activity
Concerns
Short Term
Dependence
May lead to addiction
Overdose
Mixing meth and other drugs
May lead to overdose
May lead to death
Long Term
Use during pregnancy
Infancy
Decreased arousal, increased stress, poor quality of movement
Toddler
Delayed motor development
Preschool/School-age children
Significant attention impairment, cognitive and behavioral issues in terms of self-control and executive function.
Addiction
Meth used in a binge pattern
Used every couple hours for several days to prolong high
Compulsive drug-seeking
Inability to self-regulate how much meth is used and how often
Co-occurring disorders (i.e. addiction and anxiety)
Withdrawal
Anxiety, depression, fatigue, increased appetite, psychosis
Interpersonal relationships
Violent mood swings, individual may shirk responsibilities and obligations in favor of using meth
Grades and work output drops, unemployment, financial strain, homelessness
Increased high-risk behavior and possible suicidal behavior
Medical concerns
Heart attack, brain damage coma, death
Hazardous Waste from Meth Manufacturing
Chemical Containers
Acid, drain cleaner, iodine, rubbing alcohol, starter fluid, toluene, etc.
Chemical-stained cloth and coffee filters, glassware, baking dishes, hoses, lithium batteries, propane tanks, pseudoephedrine blister packs.
Labs produce 5-7 lbs of toxic waste per pound of meth produced
Often disposed of improperly
Contaminates soil and water supplies
Other "Street Names"
Batu, Black Beauties, Blade, Cotton Candy, Dunk, Go-go juice, No Doze, White Cross, Pookie, Rocket Fuel
Chalk, Chicken Feed, Crank, Cristy, Crystal, Crystal Glass, Crystal Meth, Go Fast, Gak, Christina, Cookies
Hanyak, Hiropon, Hot Ice, Ice, Kaksonjae, LA Glass, LA Ice, Meth, Methlies, Quick, Poor Man's Cocaine, Quartz
Shards, Speed, Stove Top, Super Ice, Tina, Trash, Tweak, Uppers, Ventana, Vidrio, Yaba, Yellow Bam, Jenny Crank diet
Scooby Snax, Wash, Garbage
Meth Combined with Other Drugs
Biker Coffee, Twisters, Hugs & Kisses, Fire, Shabu,Party & Play
When Using Meth
"Getting geared up," "Chicken flippin,'" "Hot rolling," "Fried," "Foiled," "Speed freak," "Tweaking," "Scattered," "Spun out," "Zooming."
How It's Used
Medicinally (Methamphetamine Hydrochloride)
Treats attention disorders i.e. ADHD
Socially
Reduces inhibitions
Enhances confidence
Increased ability and motivation to speak with others
Traditionally
Man-made version of ephedra shrub
Ephedra has been used in Chinese
medicine for over 5,000 years
Used to treat asthma, bronchitis, hay fever, cold symptoms
Casual use to some extent
Often leads to addiction
Regulation
Schedule II of the Controlled Substances Act
Approved for pharmacological use in treating ADHD and treatment-resistant obesity
Named Desoxyn, manufactured by Ovation Pharmaceuticals
Combat Methamphetamine Epidemic Act of 2005
Regulates over-the-counter sales of ephedrine, pseudoephedrine and phenylpropanolamine (no longer OTC) because they're used in the manufacture of illegal drugs
Illegal for recreational use
Foreign Drug Cartels
Manufacture and smuggle meth over the border
Methods
Ambulances
Low probability authorities will detain emergency vehicles
Buses
Cyclists
Camouflaging it in Legal Shipments
Maritime, air and land transportation
Authorities have limited ability to inspect shipments, especially ports due to mass movement of international trade
Chemical Masking
Cartels use chemical processes to change appearance
Can be smuggled in clothes, oils,
plastics, metals, pet food, etc.
Alternative Air Transportation
Drones
Very little legislation regulating drone use
Controlled Substances Act (1970)
Regulates importation, manufacture, possession, use and distribution of meth
Mounted educational program against meth
Methamphetamine Precursor Control Policies
First began in 1983, banning possession of precursors and equipment for meth production
Federal Controlled Substance
Analogue Enforcement Act (1986)
Attempted to curb growing
use of designer drugs
Comprehensive Methamphetamine Control Act (1996)
Regulates mail order and chemical companies
selling precursor chemicals
Laws enforced by Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA)
Effects
Short Term
Hyperthermia, rapid, irregular heartbeat, increased attention, decreased fatigue, increased activity and wakefulness, euphoria and rush, increases respiration
Long Term
Addiction, paranoia, hallucination, repetitive motor activity, changes in brain structure and function, deficits in thinking and motor skills, increased distractibility, memory loss, aggressive/violent behavior, mood disturbances, severe dental problems, weight loss
Routes of Administration
Snorted
Euphoria but no intense "high"
Produces effects after 3-5 minutes
Injected
Gives and intense "rush"
Doesn't last long
Swallowed
Euphoria, but no intense "high"
Produces effects after 10-20 minutes
Smoked
Gives an intense "rush"
Doesn't last long
Inhalants
(Gasoline)
Regulation
Not federally regulated
Some states restrict sale and distribution of substances to minors that can be used as inhalants
How it's Used
Predominantly recreational use among children and adolescents
Concerns
Short Term
Overdose
Toxic reaction that leads to serious symptoms, seizures or death
Long Term
Coma, death, suffocation from use in closed spaces
Addiction
Health problems, inability to meet responsibilities at work, school or home
Withdrawal
Nausea, loss of appetite, sweating, problems sleeping, mood changes
Common Forms
Liquid that vaporizes at room temperature
Classification
Depressant
How it Works
Immediately enters the blood stream through the lungs
Slows brain function
Works similarly to alcohol, doesn't last as long
Effects
Short Term
Slurred/distorted speech, lack of coordination, euphoria, dizziness, hallucination, delusions, vomiting, drowsiness, headache
Long Term
Liver/Kidney/Brain damage, hearing loss, bone marrow damage, loss of motor control and limb spasms due to nerve damage, delayed behavioral development
Routes of Administration
Fumes inhaled by nose or mouth (i.e. gas siphoning)
Other "Street Names"
Air blast, bold, chroming, discorama, glad, hippie crack, moon gas, oz, poor man's pot, rush, snappers, whippets, whiteout, bullet bolt, highball, laughing gas
Street Names for Using Inhalants
Bagging, Huffing, Glading
Opioids
Regulation
Legal
Prescription pain killers (OxyContin, morphine, codeine, etc.)
Illegal
Heroin, illegal prescription drugs coming across the border
Federal
Federal controlled substances law affirms medical value of many drugs that are controlled substances, states that opioids may be used for extended treatment of patients with intractable pain
Providing opioids to addicts is illegal unless the physician is separately registered to treat addiction
Addendum to Harrison Law, 1919, made it illegal for physicians to prescribe opiates to treat opiate addiction
State
Permit prescribing opioids for pain, do not recognize the medical value of controlled substances
Imprecise legal definitions of terms allows patients to be confused for addicts
Some states require physicians to report opioid-dependent
Concerns
HIV risk from reusing unsterile needles
128 people a day in 2018 died from opioid overdose
Misuse and addiction of opioids is a crisis
Economic burden in the U.S. is ~$78.5 billion a year
Healthcare cost, loss of productivity, addiction treatment, law enforcement involvement
Serious issue in rural communities
Few treatment programs, low education on drug use, abuse and addiction, opioids are easy to get in rural communities
All of this affects the economy, which can increase the number of individuals using opioids
Societal costs
Loss of relationships due to addiction, loss of support from family and friends, loss of job/income
Common Forms
Natural Opiates
Alkaloids, nitrogen-containing base compounds
found in plants (i.e. opium poppy)
Morphine, codeine, thebaine
Semi-synthetic Opiates
Made from
natural opiates
Hydromorphone, hydrocodone, oxycodone, heroin (illegal)
Fully Synthetic Opiates
Completely manmade
Fentanyl (many times stronger than other opioid pain relievers), pethidine, levorphanol, methadone, tramadol, dextropropoxyphene
Classification
Agonists
Initiates physiological response
Morphine, codeine, oxycodone, pethidine, diamorphine, hydromorphone, levorphanol, methadone, fentanyl, sufentanyl, remifentanyl, tramadol, tapedolol
Antagonists
Inhibits physiological response
Naloxone, naltrexone, nalmefene, diprenorphine
Agonists/Antagonists
Nalorphene, pentazocine, nalbuphine, butorphanol, dezocine
Partial Agonists
Meptazinol, buprenorphine
Routes of Administration
Medical Routes
Oral
Preferred route and medications
are usually cheaper
Enteral Tubes
(Feeding Tubes)
Nasogastric (NG), percutaneous endoscopically placed gastrostomy (PEG) tubes, jejunal (J) tubes
Used for drug delivery if already present
Overcomes patients inability to swallow
Allows for bitter opioids like concentrated liquid morphine to be administered easily
Transdermal
Drug applied to skin to absorb slowly,
may use an adhesive patch
Only opioid available
for this route is fentanyl
Takes 12-22 hours to work
Transmucosal
Absorbed via oral mucosa
Fentanyl lozenge
Very expensive
Aerosol
Uses IV preparations in a nebulizer
Causes rapid peak blood levels
Sublingual
Goes under the tongue
Absorbed rapidly
Rectal
Used when patients can't swallow or intravenous sites are unavailable
Subcutaneous
Absorption may take longer than intravenous injection, but provides rapid pain relief without having to access a vein
Intramuscular
Injected into muscle, commonly deltoid or vastus lateralis
Not recommended for pain management, often hurts and opioids are absorbed variably and unpredictably
Intravenous
Immediately circulates systemically
Intraspinal
Injected into spaces in and around spinal cord
Morphine and fentanyl
Intrarterial
Injected directly into an artery
Local Effects
Intraperitoneal
Injected into the large surface lining the abdominal cavity
Local Effects
Pulmonary
Uses the large surface area of the pulmonary epithelium and mucous membranes
Local Effects
Cutaneous
Topical application to the conjunctiva of the eyes, nasopharynx, oropharynx, vagina, colon, urethra, and bladder
Local Effects
"Street" Routes
Oral
Most Common
Intranasal
Injection
Smoking
Least Common
Effects
Long Term
Physical dependence, tolerance, addiction
Withdrawal symptoms
Restlessness, muscle and bone pain, insomnia, diarrhea, vomiting, cold flashes with goose bumos
Short Term
Drowsiness, constipation nausea, slowed breathing, unconsciousness, coma
How it's Used
Medicinal
Used to treat moderate to severe pain
Some can be used to treat coughing and diarrhea
Recreational
Pain relief
Opioid craving
Dopamine "high"
How it Works
Binds to opioid receptors in brain, spinal cord and peripheral tissues, reducing the amount of pain messages being sent to the brain, curbing the feeling of pain, triggers the dopamine reward system
Psychedelics
Common Forms
Acid, Lysergic Acid or LSD
Developed from ergot, a mold found on rye grain
Dimethyltryptamine (DMT)
Naturally occurring, found in nuts and bark of certain trees in South and Central America
Phalaris, Delosperma, Acacia, Desmodium, Mimosa, Virola and Psychotria genera
Also found in leaves of citrus plants and leaves, seeds and inner bark of "mimosa tenuiflora," which has become a source of livestock poisoning
Has shorter effects than other psychedelics, lasts ~1 hour
Ololiuqui
Naturally occurring in morning glory seeds
Not commonly used due to unpleasant side effects
Psilocybin
Termed "magic mushrooms"
Wide variety of hallucinogenic mushrooms
Legal state is ambiguous as the are naturally found in many parts of the world
Ecstasy
Hallucinogenic properties are less pronounced, mood-altering and stimulant effects are more noticeable than in other psychedelics
Mescaline
Naturally occurring in some species of cactus (i.e. peyote)
N-Bomb
Synthetic designer drug used for neurochemistry and brain mapping
Salvia
Psychoactive drug that comes from "Salvia divinorum" a plant native to the mountains of Oaxaca, Mexico
Unique in chemical structure compared to other natural psychedelics
Not alkaloid, is terpenoid, a broad class of organic chemicals
PCP
Synthetic drug that also causes dissociative hallucinations
Originally synthesized as an anesthetic, discontinued use in humans in the 1950's
Ketamine
Precursor to PCP, synthesized for the same purpose
DXM
Common ingredient in cough suppresant
GHB
Psychoactive drug that naturally occurs in the brain
Regulation
Peyote
Schedule I drug (illegal); with religious exemptions
Listing peyote as a Schedule I drug does not apply to the nondrug use of peyote in religious ceremonies of the Native American Church
Members of the Native American Church do not have to register their peyote use when used for a religious ceremonies
Individuals manufacturing or supplying peyote to the Native American Church is required to obtain annual registration and to comply with all other law requirements
Salvia is federally legal, some states consider it a controlled substance
PCP
Not used in humans
Ketamine
Restricted to veterinary use
Concerns
Psilocybin mushrooms are difficult to distinguish from deadly mushrooms
Death Caps can look identical and grow in the same places
N-Bomb is fatal in high doses, effective dose is less than a milligram while similar synthetic hallucingoens require about 3 grams
Several overdoses caused by mistaken identity
Overdose via mistaken identity in general
How it Works
Psychedelics stimulate or suppress the activity of neurotransmitters that they are chemically similar to
Other/Street Names
Ecstasy
MDMA, molly
N-Bomb
251-NBOMe. 251
Salvia
Salvinorin A
PCP
Phencyclidine
DXm
Dextromethorpan
LSD
Acid, blotter, doses, dots, trips, mellow yellow, window pane, purple dragon
Routes of Administration
LSD
Oral
Blotter Paper
LSD soaked into sheets of absorbent paper with colorful designs, cut into small individuals dosage units
Most common form
Thin squares of gelatin
Called "window panes"
Tablets, called Microdots, or capsules
Liquid on sugar cubes
Pure liquid form
may be very potent
Sublingual
Snorting
Injection
Ecstasy
Oral
Tablet, capsule, powder and liquid
Snorting
Injection
Psilocybin
Oral
Eat them straight, brew a tea, mix them with other foods
DMT
Oral
Injection
Smoking
Peyote
Oral
Fresh or dried buttons, capsules, dried powder or a teas
N-Bomb
Snorting, sublingual and absorbed through the mucosa in the mouth
Salvia
Oral
Chewing leaves and holding them in your mouth
Smoking
Dried leaves
Effects
Effects of mescaline are similar to LSD
LSD
Alters awareness/perception, may cause hallucination, not chemically addictive, but may still cause paranoia and anxiety
Psilocybin
Increases empathy, euphoria and alters thinking. Some species may cause open and closed eye visuals
Mescaline/peyote
Color enhancements, euphoria, increase in introspection, can cause nausea and vomiting due to peyote's bitterness
Low risk of psychological addiction, not chemically addictive
Ecstasy
Increased empathy and emotional connection, elevates mood and facilitates mental and physical euphoria, can create mild hallucinations like color change and heightened audio
Causes dehydration and raises body temperature, can lead to fatal medical complications due to hyperthermia and dehydration, especially when combined with alcohol
N-Bomb
Similar to ecstasy, causes increase in empathy and affection, as well as visual hallucinations, may also cause extreme anxiety and feeling of doom
Salvia
Dissociative, distorts sight and sound, hallucinogenic effects can cause trance-like states, anxiety and dysphoria
PCP
May cause mania, delirium and disorientation, is moderately addictive and there is a possibility of developing psychological issues
Ketamine
Can cause sedation and memory loss, recreational effects are similar to PCP, also has low to moderate addiction potential
DXM
In high doses, causes dissociative hallucinogenic effects, like PCP and ketamine, less likely to cause addiction or dependence
Effects are similar to ecstasy, is habit forming in rats and may cause withdrawal symptoms
Classification
Hallucinogens
Stimulants
How it's Used
Religious
Native American Church
Uses peyote in religious ceremonies (nondrug use)
Historically
DMT used for thousands of
years by Amazonian Tribe
Activated by brewing rainforest plants in a tea
Medically
N-Bomb
Used for neurochemistry and brain mapping
GHB
Used as an anesthetic and in narcolepsy treatment