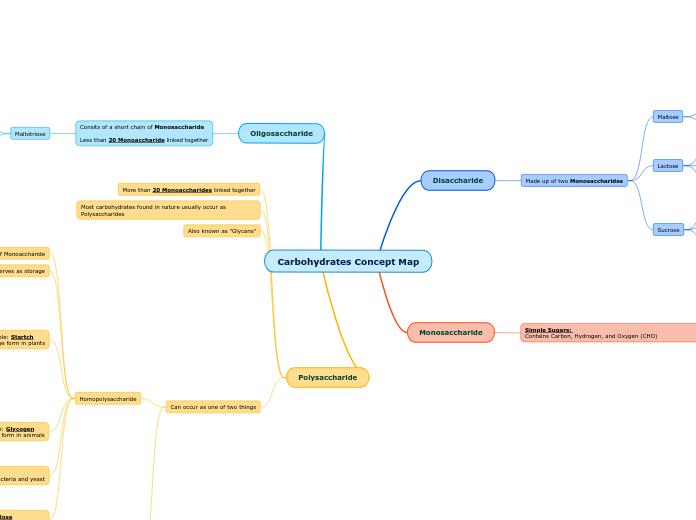
Carbohydrates Concept Map
Disaccharide
Made up of two Monosaccharides
Maltose
Two Glucose molecules which are linked together
Linked by a 1-4 a-Glycostatic bond
Lactose
Made up of 1 Galuctose and 1 Glucose
Linked by a 1-4 b-Glycostatic bond
Naturally found in Milk
Sucrose
Sucrose is made up of 1 Glucose and 1 Fauctose
Has a bond of 1 a-Glucose + 2 b-Fauctose bond
Also known as "Table Sugar"
Is formed by plants not by animals
Monosaccharide
Simple Sugars: Contains Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen (CHO)
Galactose
Glucose
Contains 6 Carbon atoms
Two types of Glucose, a-Glucose and b-Glusose
Fauctose
Oligosaccharide
Consits of a short chain of Monosaccharide
Less than 20 Monoaccharide linked together
Maltotriose
Made up of 3 Glucose molecules
Linked together by 1-4 a-Glycostatic bonds
Polysaccharide
More than 20 Monoaccharides linked together
Most carbohydrates found in nature usually occur as Polysaccharides
Also known as "Glycans"
Can occur as one of two things
Homopolysaccharide
Contains only a single type of Monoaccharide
Serves as storage
Example: Startch
Storage form in plants
Only made up of Glucose
Amylose
Unbranched Glucose Polymer
Contains 1-4 a-Glycostatic bonds
Amylopectin
Branched Glucose Polymer
Contains 1-4 and 1-6 a-Glycostatic bonds
Branch points occur every 24-30 glucose residues
Example: Glycogen
Storage form in animals
Made up of only Glucose
Contains 1-4 and 1-6 a-Glycostatic bonds
Branch points occur every 8-12 glucose residues
(Occurs more frequently)
Example: Dextran
Structural component in bacteria and yeast
Made up of a 1-3 and a 1-6 Glycostatic bonds
Possible it can contain a 1-2 and a 1-4 Glycostatic bonds
Example: Cellulose
Structural components in plants
Make up the plant cell wall
Made up of b 1-4 linked glucose residues
Humans do not have enzymes that hydrolyze b 1-4 Glycostatic bonsa
Heteropolysaccharide
Contains two or more differnt types of Monoaccharides