CASLA THROUGH A SOCIAL CONSTRUCTIVIST PERSPECTIVE
References
Simina, V., & Hamel, M. J. (2005). CASLA through a social constructivist perspective: WebQuest in project-driven language learning. ReCALL, 17(2), 217-228.
Dodge, B. (1995) Some thoughts about WebQuests. http://edweb.sdsu.edu/courses/edtec596/
about_webquests.html
Aydin, S. (2016). WebQuests as language-learning tools. Computer Assisted Language Learning, 29(4), 765-778.
A paradigm
in which
Learners become
a centre of learning
people with
prior knowledge

Second language learners
Computer technology

this is supported by
Several theories
such as
Constructivism
A more individual focus
People construct knowledge by their own
its biggest contributor
Social construtivism
culture and context
its representative
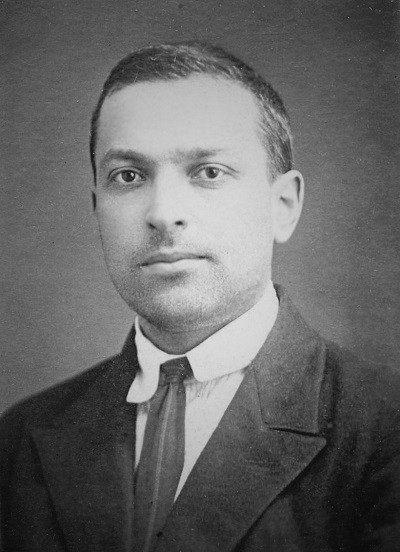
Lev Vigotsky

ZPD
Scaffolding
the activities provided by the
educator to support the student
The distance between
what a person know
what he/she does not know
embrace
what I can learn on my own
what I can learn with help
as an example
Knowledge other
Technology tools
beyond my reach
"Cognitive operations originate in social
interactions and emphasized the role of language and culture in cognitive development as frameworks through which humans experience, communicate and understand reality." (Simina & Hammel, 2005)
An approach
Two theorical frameworks
Knwoledge is created
by
Cognitive aspect

The experiences are
the base of learning
Social aspect

Social interaction as essential
in the construction of knowledge
some important
acronyms
CASLA: Computer Applications in Second Language Acquisition.
SLA: Second Language Acquisition.
CALL: Computer Assisted Language Learning.
ZPD: Zone of proxime development.
L1: Mother tongue.
L2: Second language.
A new project

CALL environment
SLA

several factors converge
such as
Cultural Capital
the skillis, education,
norms and behaviuos
members of a social group
can give economic
and other advantages
resources to learn
another language
Constructivism
Knowledge is construted
with prior information
Student has prior knowledge of L2
His/her L1
This gives a global idea of L2
Universal Grammar
Social Constructivism
Ideal characteristics
that fosters
Cognitive apprenticeship
Situated leraning or cognition
Collaborative learning
how learners create a new language system
some conditions
as
Input
what learners
are exposed to
what they receive
reading and listening
known as
Four skills of
communicative
competence
Output
what they produce
speaking
and writing
an strategy of learning
that provides
Plenty of ideal input/outp
Opportunity for focus
in
structure
cognitive aspect of learning
Linguistics
meaning
social aspect of learning
semantics and pragmatic
Opportunity for noticing errors
Modified interaction between learner and computer
WebQuest

a multimodal model
connect and engage students
contextualized language
and research tasks
"WebQuest use improves interaction, communication, critical thinking, knowledge application, social skills, scaffolded learning, higher order thinking skills and problem-solving skills" (Aydin, 2016)
"An inquiry oriented activity in which some or all the information that learners interact with comes from the Internet" (Dodge, 1995)
Jean Piaget
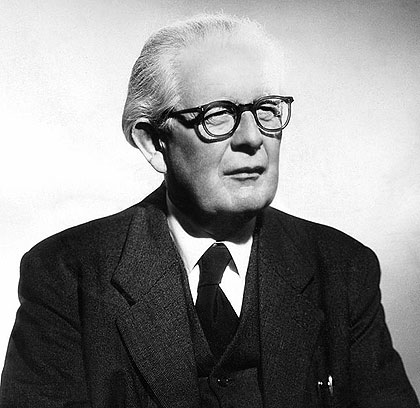

"Individuals construct their knowledge through their interaction with their social and physical environment and by reflecting on their experiences." (Simina & Hammel, 2005)
The term of squemata
/GettyImages-1126484970-ee992b9c471340afb7f0634bd03fada9.jpg)
a pattern of thoughs or behaviors
categories of informarion
the relationships among them
The culture
meaning
how humans perceive the world
a process
Somebody sense something
pay attention
recall information
active the adecquate schema
respond