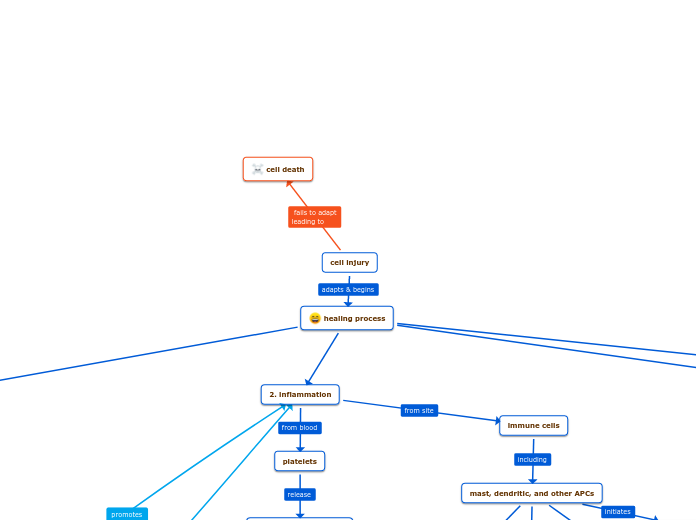
cell injury
cell death
healing process
1. hemostasis
vessel spasm/smooth muscle reaction
platelets come into contact with collagen
activation and aggregation of platelets
blood coagulation
extrinsic
tissue factor
Activated X
prothrombinase = common
prothrombin
thrombin
fibrinogen
loose fibrin threads
strengthened fibrin threads
clot formed
Activated XIII
intrinsic
Activated platelets
platelet phospholipids
Activated XII
Activated X
cytokines
histamine
vasodilation
&
capillary permeability
chemotactic factors
leukocyte infiltration
cytokines & GFs
keratinocytes
stored IL-1s
2. inflammation
platelets
blood-clotting proteins
immune cells
mast, dendritic, and other APCs
vessel dilation &
constriction factors
exudate to area &
increase edema
leukoctyes to site
neutrophils
bacteria & debris
macrophages
cytokines
histamine
vasodilation
capillary permeability
chemotactic
factors
leukocytes to
area of
phagocytosis
platelet activating
factors
platelet
aggregation
leukocyte adhesion
to endothelium
interleukins
immune response
interferons
unwanted
DNA/RNA
replication
tumor necrosis
factor alpha
proinflammatory
effect
arichidonic acid
derivatives
leukotrines
smooth
muscle
contraction
prostaglandins
neutrophil chemotaxis
pain receptors
cascade by degranulating
3. proliferation
epithelial cells
vascularization
new blood supply
repithelialization
horizontal
mitotic
growth
vertical
differentiation
fibroblasts
damage to CT
granulation tissue components
collagen type III
glycosaminoglycans
fibronectin
elastin
tissue fibroblasts
GFs
4. maturation
regeneration
original structure
& function
repair
reconstruction
collagen
type III to I
crosslinking
maturation
myofibroblasts at damaged area
new CT
fibrous elements
smaller opening/skin stretched