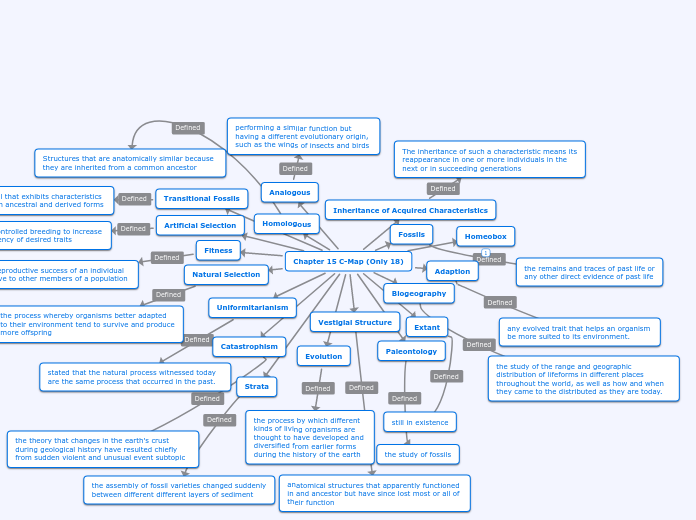
Chapter 15 C-Map (Only 18)
Evolution
the process by which different kinds of living organisms are thought to have developed and diversified from earlier forms during the history of the earth
Vestigial Structure
anatomical structures that apparently functioned in and ancestor but have since lost most or all of their function
Paleontology
the study of fossils
Extant
still in existence
Strata
the assembly of fossil varieties changed suddenly between different different layers of sediment
Catastrophism
the theory that changes in the earth's crust during geological history have resulted chiefly from sudden violent and unusual event subtopic
Uniformitarianism
stated that the natural process witnessed today are the same process that occurred in the past.
Biogeography
the study of the range and geographic distribution of lifeforms in different places throughout the world, as well as how and when they came to the distributed as they are today.
Natural Selection
the process whereby organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring
Fitness
the reproductive success of an individual relative to other members of a population
Adaption
any evolved trait that helps an organism be more suited to its environment.
Artificial Selection
human-controlled breeding to increase the frequency of desired traits
Fossils
the remains and traces of past life or any other direct evidence of past life
Transitional Fossils
a fossil that exhibits characteristics of both ancestral and derived forms
Homologous
Structures that are anatomically similar because they are inherited from a common ancestor
Analogous
performing a similar function but having a different evolutionary origin, such as the wings of insects and birds
Homeobox
Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics
The inheritance of such a characteristic means its reappearance in one or more individuals in the next or in succeeding generations