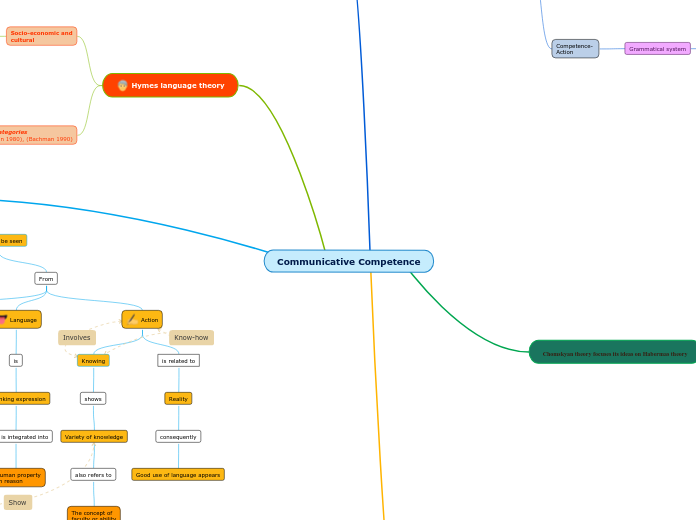
Communicative Competence
Linguistic competence (Chomsky)
Mental process
Innate abilities
Therefore
Native language.
Unconscious process
Transformational-Generative Grammar
Universal genetic programming
Universal-grammar
Individual-use
Competence-
Action
Grammatical system
Intented
Communication
Social Interaction
Habilities
Knowledge
Chomskyan theory focuses its ideas on Habermas theory
Communicative Action
Search
Understanding
Aimed at the
Communicative rationality
that sets up
Communication structure
With
Acts of speech
It is characterized
Condition of validating the Dialogue
I mean
Understanding with someone about something
Universal Pragmatic
Implies
Understanding words in terms of action
I mean
The meaning of words occurs in communicative interactions
Members: Edna Avendaño Naranjo, Daymar Gabriela García, Sofia Mora Torres, Samantha Noy and Laura Natalia Castañeda.
Hymes language theory
Socio-economic and
cultural
Uses of language
Competence is:
Attitude
Values
Motivations
Social-experience
Language subcategories
(Canale and Swain 1980), (Bachman 1990)
Grammatical competence
Sociolinguistics
Discursive
Communicative and strategic
COMPETENCE
Arises as an alternative to
School processes
Curricular components
Evaluation
Needs to be seen
from
The Greek thought
on
Construction of
knowledge
Nature
From
Thinking
builds
Knowledge
appears as
Human actions and Human faculties
Language
is
A thinking expression
And it is integrated into
A human property
with reason
Action
Knowing
shows
Variety of knowledge
also refers to
The concept of
faculty or ability
is related to
Reality
consequently
Good use of language appears