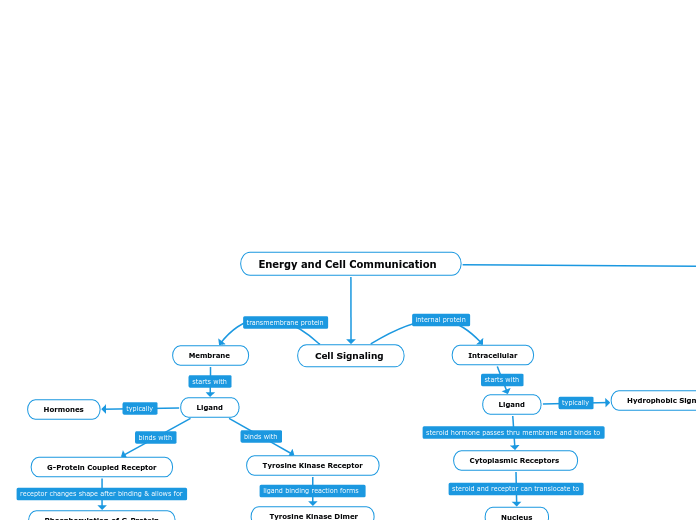
Energy and Cell Communication
Cell Signaling
Membrane
Ligand
G-Protein Coupled Receptor
Phosphorylation of G-Protein
Activated G-Protein
Enzyme (Adenylyl Cyclase)
cAMP (second messenger)
Protein Kinase A
Cellular Response
Regulation of Cellular Activities
Tyrosine Kinase Receptor
Tyrosine Kinase Dimer
Tyrosine Phosphorylation
Fully Activated Tyrosine Kinase Receptor
Relay Molecules
Protein Kinase 1
Protein Kinase 2
Active Protein
Cellular Response
Regulation of Cellular Activities
Hormones
Intracellular
Ligand
Hydrophobic Signaling Molecule
Cytoplasmic Receptors
Nucleus
Gene Expression Regulation
Energy in plants is made through photosynthesis
found in Mesophyll
Contains 30-40 chloroplasts
Stomata-
- takes in CO2 and removes O2
2 stages
Stage 1 (light reactions)
H2O splits into electrons and H+ protons
O2 released
NADP+ reduced
ATP through photophosphorylation
Thylakoid
Photosystem I
light enters
electrons from ETC enter
electrons jump to exited state from ground state over and over
electrons go into special pair that absorbs light at 700 nm
primary acceptor
ferredoxin
NADP+ reductase
produces NADPH
Photosystem II
H2O enters
light enters
electrons chain through
electrons jump to exited state from ground state over and over
electrons go into special pair that absorbs light at 700 nm
primary acceptor
Electrons sent down ETC
cytochrome complex
plastocyanin
Cyclical flow
Non cyclical flow
Stage 2 (Calvin Cycle)
Calvin cycle makes sugar
CO2 is fixed through carbon fixation
ATP provides energy, NADPH provides electrons
Alternatives for carbon fixation
C4
CAM
Calvin Cycle
3 CO2 enter
use enzyme Rubisco to fixate carbon
Adds to Ribulose bisphosphate
eventually releases sugar
Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis
cell cytosol
splitting of sugar
under anaerobic conditions
glucose
glucose-6-phosphate
fructose-6-phosphate
fructose-1,6-diphosophate
using 2NAD+
2NADH
releases energy
4 substrate level phosporylations
2 NADH
key process
fermentation
cytoplasm
ethanol
lactic acid
lactic acid buildup
4 ATP
2 net ATP
Pyruvate Oxidation
pyruvate dehydrogenase
2 pyruvate
decarboxylation
oxidation
2NAD+
2NADH
attachement
acetyl CoA
final product for channeling energy
matrix of mitochondira
Citric Acid Cycle
2 acetyl coA
2 oxaloacetate
2 citrate
changes to its structure
products
2FAD2
4CO2
6NADH
2ATP
Oxidative Phosphorylation
electron transport chain
chemiosmosis
concentration gradient
ATP syntahse
protons
liberates energy
phosphorylate ADP to ATP
intermembrane space
mitochondrion
cristae
reduces coenzymes
NADH
3 ATP
FADH2
2 ATP
electron acceptors
cytochromes
transmembrane
NADH dehydrogenase
ubiquinone
cytochrome oxidase complex
oxygen
final electron receptor
protons
water
least to most electronegative
redox reactions
protons released
free energy
actively pump protons from matrix to outer compartments
to generate ATP
36 net ATP
substrate-level phosphorylation
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
ATP formed directly
inorganic phosphate
ADP
energy released cause reactants to join
ATP
oxidative phosphorylation
electrons
reduced coenzyme
electron transport chain
redox reactions
oxygen
the final electron receptor
harvest energy from organic compounds
oxidizing glucose
small amounts of energy being released at a time
C6H12O6
6CO2
6O2
6H20
exothermic
catabolic