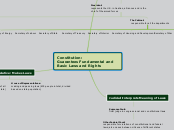
Constitution:
Guarantees Fundamental and Basic Laws and Rights
Legislative: Makes Laws
Senate:
responsible for protection the interest and rights of all citizens through laws (100 people in total, 2 per state)
House of Representatives:
making and passing laws (435 people in total, divided based on state population)
Executive: Enforces Laws
President:
represents the U.S. in treaties, alliances and is the chief of the armed forces
Vice President:
assists the President and presides over the Senate
The Cabinet:
responsible for all the departments
secretary of agriculture
Secretary of Energy
Secretary of Labour
Secretary of State
Secretary of Treasury
Secretary of Interior
Secretary of Housing and Development
Secretary of War
Secretary of Health and Human Services
Secretary of Veterans Affairs
Secretary of Transportation
Secretary of Commerce
Secretary of defense
Judicial: Interprets Meaning of Laws
Supreme Court:
final judge in congressional and constitutional laws
Other Federal Court:
responsible for violations of constitutional and federal laws; also cases between citizens of different states