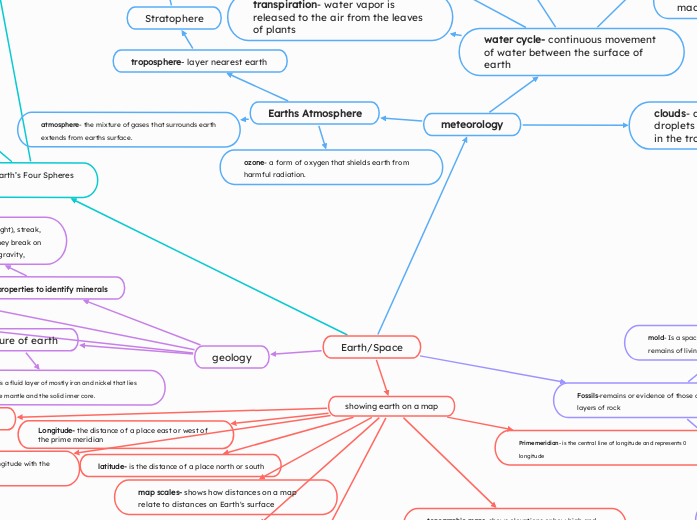
Earth/Space
showing earth on a map
Longitude- the distance of a place east or west of the prime meridian
latitude- is the distance of a place north or south
parallels- lines of latitude
Prime meridian- is the central line of longitude and represents 0 longitude
Equator- divides earth into two parts
International date line- the line of longitude with the highest number value 180 east and w
map scales- shows how distances on a map relate to distances on Earth's surface
map legends- list the symbols used on a map and explains their meaning.
topographic maps- shows elevations or how high and low a area is.
Contour lines- connects points that have the same elevation.
index contours- show elevations and are darker then other contour lines.
geology
structure of earth
crust- the outermost layer
mantle- the thickest layer of the planet, located between the crust and the outer core
outer core-is a fluid layer of mostly iron and nickel that lies between the mantle and the solid inner core.
inner core- is a fluid layer of mostly iron and nickel that lies between the mantle and the solid inner core.
minerals- a naturally formed solid substance with crystal structure
crystal structure- a definite pattern in the way particles in a substance are arranged
properties to identify minerals
hardness, color, luster( how it reflects light), streak, crystal shape, cleavage and fracture(they break on how atoms are arranged and specific gravity,
Fossils-remains or evidence of those organism in layers of rock
petrified fossil- forms when minerals replace the bone, shell or other hard part that was trapped.
trace fossils- include the footprints, tracks, trails and burrows.
cast- is a model in the shape of a living thing or its remains.
mold- Is a space in a rock that has shape of the remains of living things that once occupied the space.
Coprolites- are the petrified remains of animal dung.
imprints- are impressions of parts of organisms left in the soil.
meteorology
Earths Atmosphere
atmosphere- the mixture of gases that surrounds earth extends from earths surface.
ozone- a form of oxygen that shields earth from harmful radiation.
troposphere- layer nearest earth
Stratophere
mesosphere
theremosphere
exoshere- outermost layer
water cycle- continuous movement of water between the surface of earth
evaporation- process in which liquid water changes into invisible water vapor in the form of gas.
transpiration- water vapor is released to the air from the leaves of plants
condensation- Is the process in which water vapor changes into liquid water.
precipitation- occurs when water or a from of ice falls from the atmosphere to Earth's surface.
clouds- are masses of water droplets or ice crystals that hang in the troposphere.
Cirrus- wispy, feathery clouds made of ice crystals.
cumulus- puffy clouds
nimbo- rain cloud.
alto- middle altitude
Stratus- sheet like clouds
Earth’s Four Spheres
Geosphere-comprises the solid Earth and includes both Earth’s surface and the various layers of the Earth's interior.
Atmosphere: gaseous envelope that surrounds the Earth and constitutes the transition between its surface and the vacuum of space
Hydrosphere: includes all water on Earth (including surface water and groundwater)
Biosphere: the life zone of the Earth and includes all living organisms, and all organic matter that has not yet decomposed.