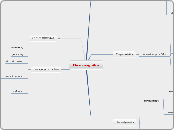
Electromagnetism
ABOUT THIS MAP
Electrostatics
constant electric fields
electric charge (q)

electric field
electric potential (V)
electrical potential energy (U)

Coulomb's Law - discrete case
electric dipole
electric dipole moment (qd)
electric charge density (/rho)
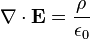
Gauss' Law

Coulomb's Law - continuous case
Magnetostatics
constant magnetic fields
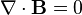
no magnetic monopoles
magnetic dipole
torque
change in magnetic potential energy
magnetic field (B)
magnetic flux (phi)
Biot-Savart Law
Electrodynamics
moving charges
electric current (I)
current density (J)
Ohm's Law
resistance (R)
resistivity
electronic networks/circuits
acccelerating charges
radiation
electromagnetic waves
Lorentz Force equation
induced fields
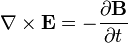
Faraday's Law of induction
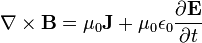
Ampère's Law
as history progresses, understanding grows...
and electricity and magnetism are united by:
Maxwell's Equations
concepts yet to include
susceptibility
permittivity
dielectric constant
magnetic materials
ferromagnetism
paramagnetism
diamagnetism
...and more!