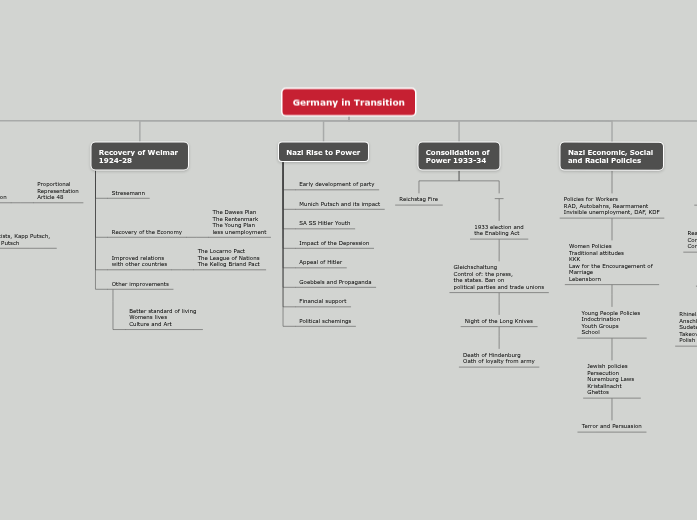
Germany in Transition
Weimar 1919-1923
Weaknesses of the Weimar Consitution
Proportional
Representation
Article 48
Impact of the Treaty of Versailles
Political Instability
Spartacists, Kapp Putsch,
Munich Putsch
Events in the Ruhr
and Hyerinflation 1923
Recovery of Weimar
1924-28
Stresemann
Recovery of the Economy
The Dawes Plan
The Rentenmark
The Young Plan
less unemployment
Improved relations
with other countries
The Locarno Pact
The League of Nations
The Kellog Briand Pact
Other improvements
Better standard of living
Womens lives
Culture and Art
Nazi Rise to Power
Early development of party
Munich Putsch and its impact
SA SS Hitler Youth
Impact of the Depression
Appeal of Hitler
Goebbels and Propaganda
Financial support
Political schemings
Consolidation of
Power 1933-34
Reichstag Fire
1933 election and
the Enabling Act
Gleichschaltung
Control of: the press,
the states. Ban on
political parties and trade unions
Night of the Long Knives
Death of Hindenburg
Oath of loyalty from army
Nazi Economic, Social
and Racial Policies
Policies for Workers
RAD, Autobahns, Rearmament
Invisible unemployment, DAF, KDF
Women Policies
Traditional attitudes
KKK
Law for the Encouragement of
Marriage
Lebensborn
Young People Policies
Indoctrination
Youth Groups
School
Jewish policies
Persecution
Nuremburg Laws
Kristallnacht
Ghettos
Terror and Persuasion
Hitler's Foreign
Policy
Foreign Policy Aims
Rearmanent and
Conscription. Disarmament
Conference
Stresa Front 1935
Rhineland remilitarised 1936
Anschluss 1938
Sudetenland Crisis 1938
Takeover of Czechoslovakia 1939
Polish Corridor 1939
Non- Agression Pact
with Poland 1934
Rome Berlin Axis 1936
Anti-Comintern Pact 1936
Pact of Steel 1939
Nazi Soviet pact 1939