Hierachy

Immune System
Thymus
Epithelial tissues
columnar cells
cuboidal cells

squamous cells
Lymphatic Tissues
lymphocytes
macrophage cells
reticular cells

Bone Marrow
Stromal

Stromal cells
Mesenchymal stem cells
hemopoietic
Hematopoietic stem cell
White blood cell

Spleen
White pulp
T cell
Red pulp

Red Blood Cells
Plasma
granulocytes

Tonsils
Lymphatic Tissues
lymphocytes

macrophage cells
reticular cells

Lymph Nodes
Lymphatic Tissues
lymphocytes
macrophage cells

reticular cells
Dense connective tissue
Fibroblast cells
Collagen fibers

Elastin fibers

Lymphatic System
Tonsils
Lymphatic Tissues
lymphocytes
macrophage cells

reticular cells
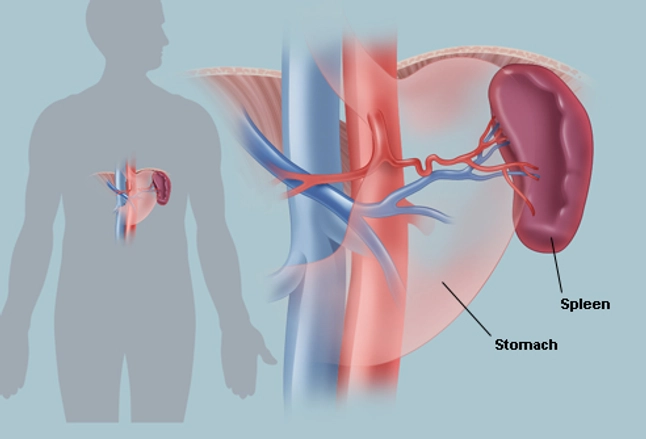
Spleen
White pulp

T Cells
Red pulp
Red Blood Cells
Plasma

granulocytes

Thymus
Lymphatic Tissues
lymphocytes
macrophage cells
reticular cells
Epithelial tissues
columnar cells

cuboidal cells
squamous cells

Appendix
Lymphatic Tissues
lymphocytes
macrophage cells
reticular cells
Lymph Nodes
Lymphatic Tissues
lymphocytes

macrophage cells
reticular cells
Dense connective tissue
Fibroblast cells
Collagen fibers
Elastin fibers
Bone Marrow

hemopoietic
Hematopoietic stem cell
White blood cell
stromal
Stromal cells

Mesenchymal stem cells
Musculoskeletal system

Bones

Bone Tissue
osteoblasts
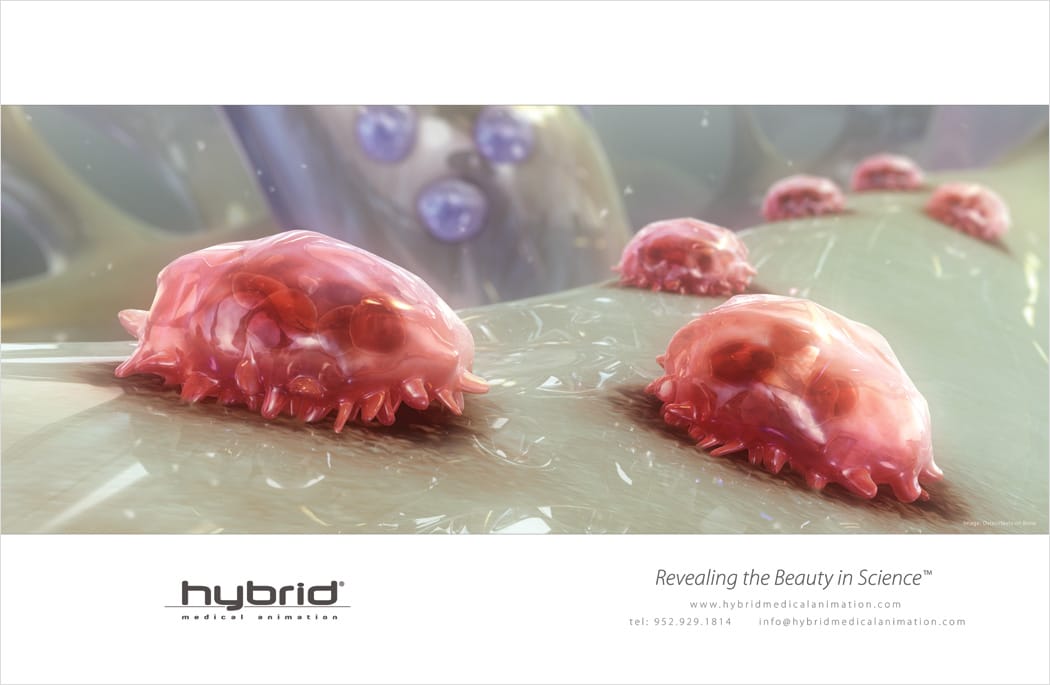
osteoclasts
osteocytes
osteoprogenitor
Connective tissue
Fibroblast

Mast cells
Plasma cells
Bone Marrow
hemopoietic
Hematopoietic stem cell
White blood cell
stromal
Stromal cells

Mesenchymal stem cells

Muscles
Skeletal muscle tissue

Skeletal muscle cells
Smooth muscle tissue
Smooth Muscle Cells

Cardiac muscle tissue
Cardiac Muscle Cells
The immune system is made up of a network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body against infection and maintain overall health.
Vaccines work by stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies against a foreign invader without actually infecting the individual with the disease.