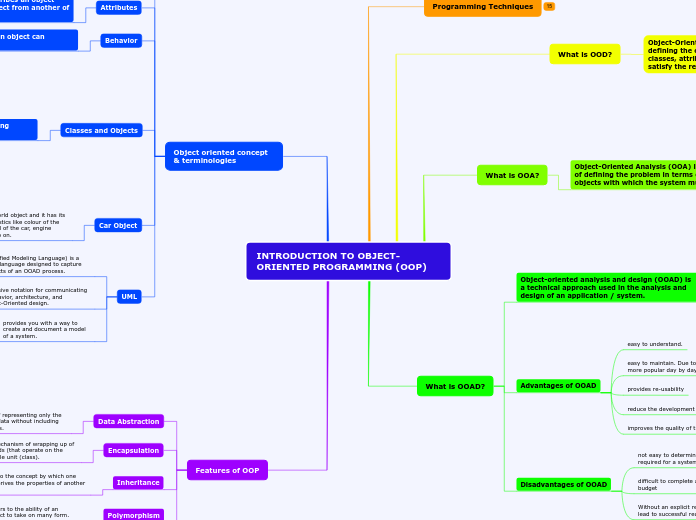
INTRODUCTION TO OBJECT- ORIENTED PROGRAMMING (OOP)
Programming Techniques
What is OOD?
Object-Oriented Design (OOD) is the process of defining the components, interfaces, objects, classes, attributes, and operations that will satisfy the requirements.
The implementation details generally include
Restructuring the class data
Implementation of methods
Implementation of control
What is OOA?
Object-Oriented Analysis (OOA) is the process of defining the problem in terms of real-world objects with which the system must interact.
The primary tasks in OOA are
Identifying objects
Organizing the objects
Defining the object attributes
Defining the behaviour/ function of the objects
Describing how the objects interact
It clarifies and documents the requirements of a system.
What is OOAD?
Object-oriented analysis and design (OOAD) is a technical approach used in the analysis and design of an application / system.
Combination of OOA and OOD approach
applied throughout the development life cycle to foster better product quality and even encouraging stakeholder participation and communication.
and even encouraging stakeholder participation and communication.
Advantages of OOAD
easy to understand.
easy to maintain. Due to its maintainability OOAD is becoming more popular day by day
provides re-usability
reduce the development time & cost
improves the quality of the system due to program reuse
Disadvantages of OOAD
not easy to determine all the necessary classes and objects required for a system
difficult to complete a solution within estimated time and budget
Without an explicit reuse procedure this methodology do not lead to successful reuse on a large scale
Object oriented concept & terminologies
Object
An instance or specific example of a class.
Example
If Cat is the class, then Betsy, Ladi, Patches, Jake, Radar, and Frosty are specific instances of the class found in my house
Attributes
Data value or state that describes an object and helps you to tell one object from another of the same class
Behavior
operation or function that an object can perform.
Classes and Objects
Classes and objects are building blocks of OOP approach.
Class
A class is a template or blueprint to create an object.
Object
Is an instance of a class.
Characteristics of real world object are variables or data members in a class.
Behaviour of objects are called as methods or member functions of a class.
Subtopic
Subtopic
Car Object
Car is a real world object and it has its own characteristics like colour of the car, size, model of the car, engine capacity and so on.
UML
UML (Unified Modeling Language) is a graphical language designed to capture the artifacts of an OOAD process.
provides a comprehensive notation for communicating the requirements, behavior, architecture, and realization of an Object-Oriented design.
provides you with a way to create and document a model of a system.
Features of OOP
Data Abstraction
Refers to the concept of representing only the essential features of a data without including the non-essential details.
Encapsulation
Refers to the mechanism of wrapping up of data and methods (that operate on the data) into a single unit (class).
Inheritance
Refers to the concept by which one class derives the properties of another class.
Polymorphism
Refers to the ability of an object to take on many form. Eg: buttons on remote control.