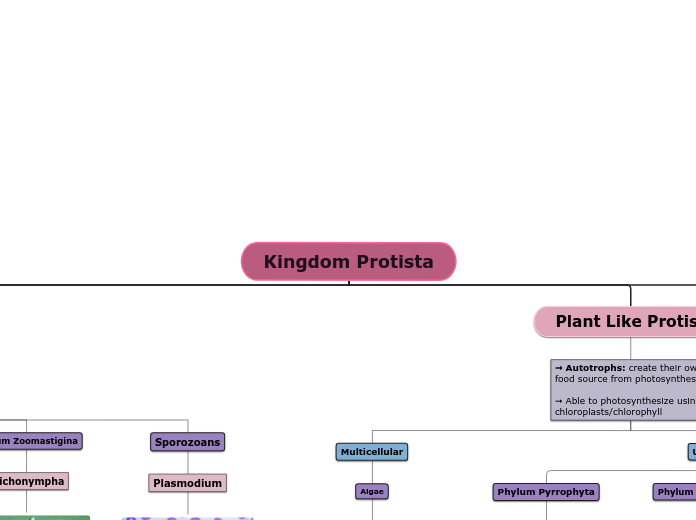
Kingdom Protista
Protists
A eukaryotic organism
usually unicellular, that is not a fungus, plant, or animal
(miscellaneous group)
Characteristics
➞ Eukaryotic
➞ Most are unicellular
(except algae)
➞ Grouped based on nutrition
(heterotrophs or autotrophs)
➞ Protists use cilia, pseudopods,
or flagella to move
➞ Most protists are single-celled.
➞ Some are multicellular but
do not form trust tissues
Reproduction
Most reproduce asexually
sometimes sexually
Animal Like Protist
➞ Heterotrophs: consume
other prokaryotes
➞ Some are parasitic
Phylum Cercoza
Amoeba
Diseases
Entamoeba
hystolitica causes
amoebic dynastry
Habitat
Decaying vegetation
in fresh or salt water
or in animals
Movement
Has pseudopods
Amoeba Proteus 40x
Amoeba Proteus 100x
Amoeba Proteus 400x
Phylum Cilliophora
Paramecium
Diseases
Balantidium coli: causes
diarrhea in humans, only
ciliate parasite in humans
Habitat
Aquatic environments
Movement
Has cilates
Paramecium 40x
Paramecium 100x
Paramecium 400x
Phylum Zoomastigina
Trichonympha
Habitat
the hindgut of lower
termites and wood
roaches
Movement
Has flagellates
Sporozoans
Plasmodium
Subtopic
Habitat
Sporozoans primarily
live in the blood cells
or other organs like
the muscles or kidneys
Diseases
Causes life
threatening malaria
Plant Like Protist
➞ Autotrophs: create their own
food source from photosynthesis
➞ Able to photosynthesize using
chloroplasts/chlorophyll
Multicellular
Algae
Spirogyra 40x
Spirogyra 100x
Spirogyra 400x
Unicellular
Phylum Pyrrophyta
Dinoflagellates
➞ Some species
cause red tides
(can be harmful
to humans)
➞ Bioluminescence
Symbiodinium
Phylum Chrysophyta
Diatoms
➞ Diverse and
abundant
phytoplankton
➞ Food source for
marine animals
➞ Rigid cell walls with
outer layer of silica
Diatoms
Phylum Euglenozoa
Euglenoids
➞ Autotrophs in sunlight
➞ Heterotrophs in the dark
➞ Has an eyespot to detect
light
Euglena 40x
Euglena 100x
Euglena 400x
Fungus Like Protists
➞ Heterotrophic: absorbs
nutrients from living and
dead organisms and waste
➞ Produces spores like fungi
Phylum Myxomycota
Plasmodial Slime Mould
➞ Slug like, creep over
decaying material
➞ Has streaming blobs
that contain many
nuclei
Subtopic
Phylum Acrasiomycota
Cellular Slime Mould
➞ Individual amoeboid
cells, 1 nucleus each
➞ Ingests bacteria or
yeast
➞ Pseudoplasmodium
forms when food is
scarce
Subtopic
Phylum Oomycota
Water Mould
➞ Filamentous
➞ Some parasitic
(extend threads into host
tissues and absorb nutrients)
Subtopic