Levels of organization of life
Biological
Concept
In the body of a living being there are different structures that are organized according to their complexity. This level constitutes the set of tissues that has competence at the individual level to exchange energy and matter with the environment, and to replicate itself.
There are 6 sub levels
Organell
An organelle is a specific structure within a cell. There are many different types of organelles. Organelles are also called vesicles.

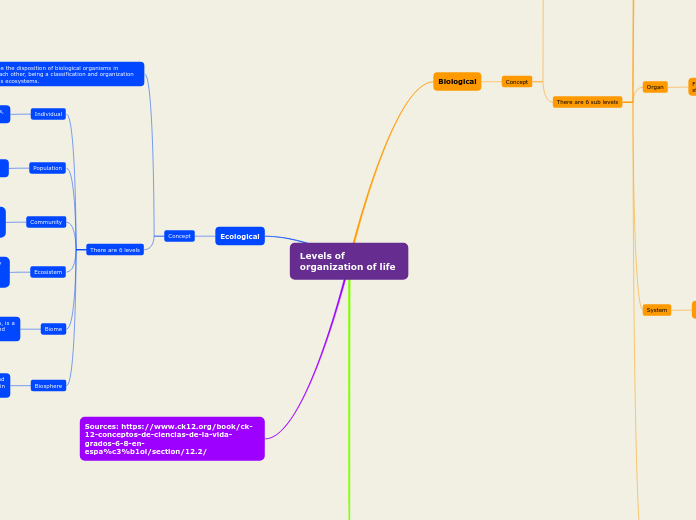
Cell
It is the smallest unit that can live on its own and forms all living organisms and tissues in the body. The three main parts of the cell are the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm.
Eukaryotics
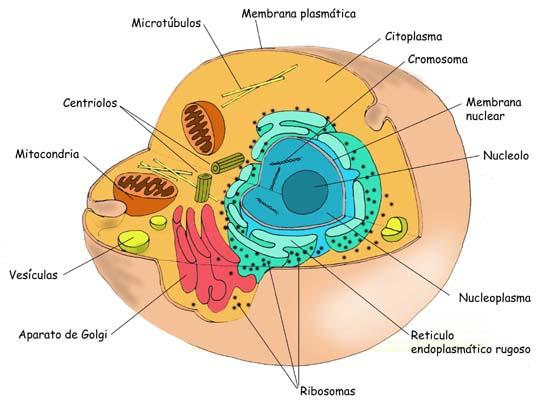
Procariotics
Tissue
Are those biological materials made up of a complex and organized set of cells, of one or several types, regularly distributed with a coordinated physiological behavior and a common embryonic origin.
Conective tissue

Epitelial tissue

Muscular tissue
Nervous tissue
Organ
Functional unit of a multicellular organism that constitutes a structural unit and performs a specific function.
Some of there examples are
Heart

Brain

Kidney

System
it is a complex network of relevant biological entities. Usually used to refer to the human organ and tissue system
Some of there examples are
Respiratory system

Digestive system

Circulatory system

Organism
Living being to a singular and differentiated individual, composed of a set of hierarchical and specialized organic matter.
Some of there examples are
Human

Animal

Fungi

Chemical
Concept
The elements that from and conform the matter and it's interactions, without altering their structure. Is the lowest level in this organization, they combine each other to form more complex organisms.
There are 3 sub levels
Subatomic
The matter is organized in protons, electrons and neutrons
Atomic
The chemical characteristics of each atom that can bind to others and form substances
Molecular
The combination of two or more atoms gives rise to the formation of simple or complex molecules
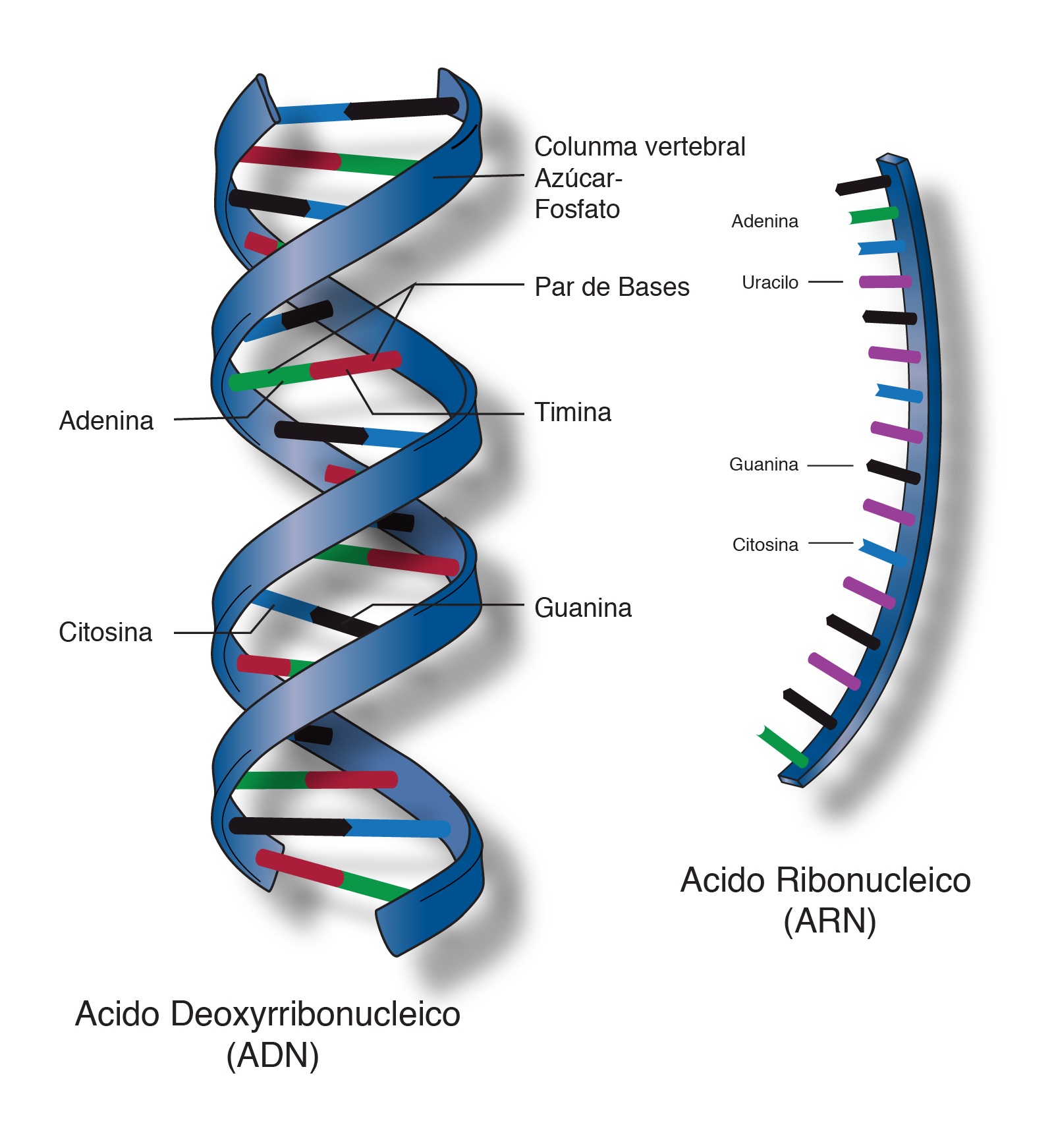
Biomolecular
They are the constituents of cellular structures
Lipids

Carbohydrates

Proteins

Nucleic acids
Ecological
Concept
They describe the disposition of biological organisms in relation to each other, being a classification and organization of the various ecosystems.
There are 6 levels
Individual
Living being, animal or plant, belonging to a species or genus, considered independently of the others.
Human

Population
are all organisms of the same group or species, living in a particular geographic area
New York City

Community
A community is a group of human beings who have certain elements in common, such as language, customs, values, tasks, worldview, age, geographic location, social status or roles.
A forest of trees

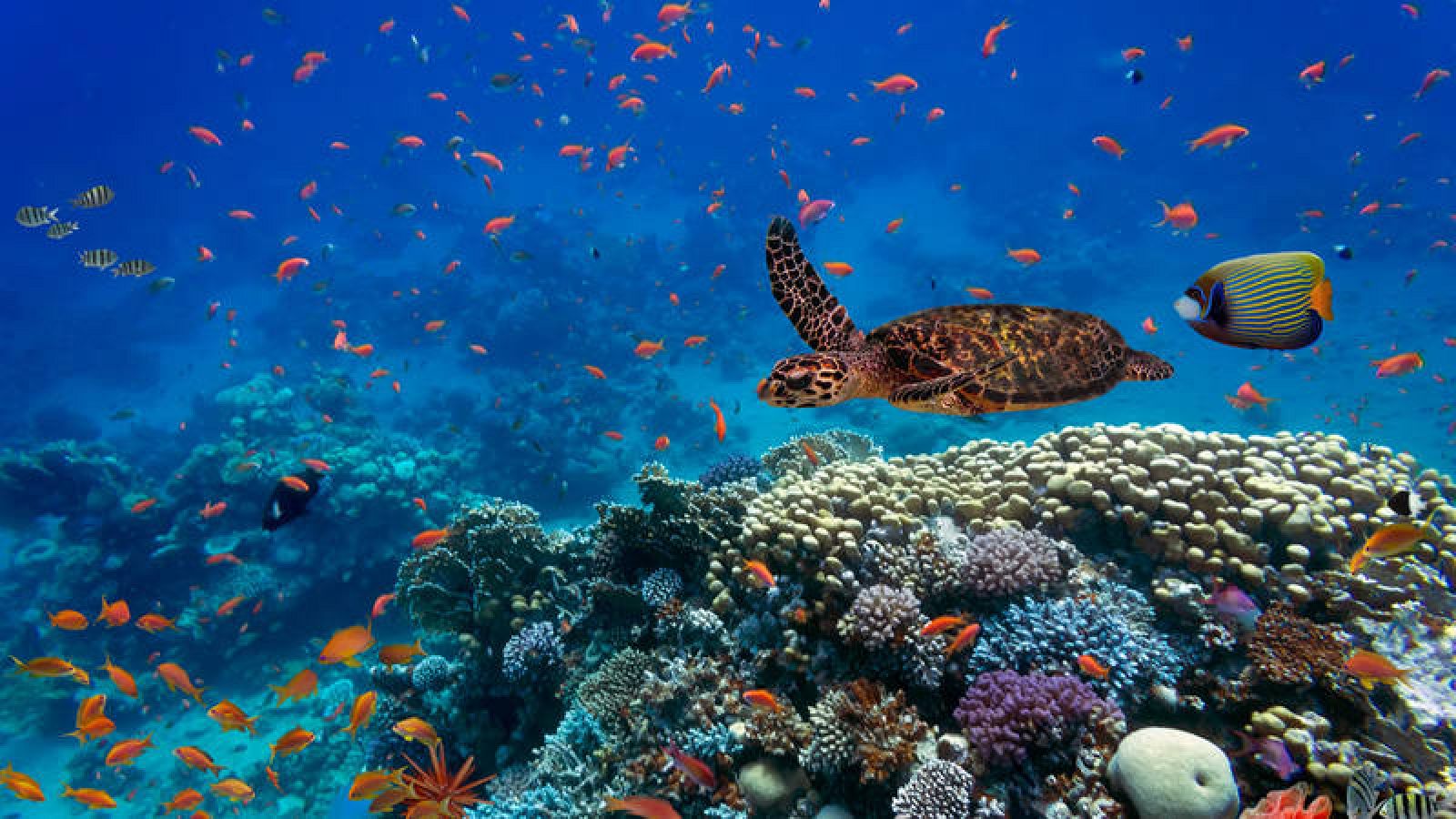
Ecosistem
An ecosystem is a biological system made up of a community of living organisms and the physical environment in which they are related, it is a unit composed of interdependent organisms that share the same habitat.
Marine ecosystem

Biome
A biome, also called a bioclimatic landscape or biotic area, is a certain part of the planet that shares the climate, flora and fauna.
Grassland

Biosphere
the system formed by all the living beings on planet Earth and their interrelationships, sometimes to refer to the space within which life develops.